Fig. 6.
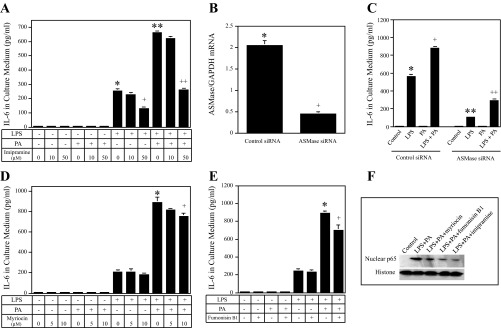
The effect of imipramine (IMP), myriocin, fumonisin B1, and acid sphingomyelinase (ASMase) knockdown on IL-6 secretion induced by LPS, PA, or both LPS and PA. Bars with different symbols in the bar graphs have significantly different values. A: RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 1 ng/ml LPS, 100 μM PA, or both LPS and PA in the absence or presence of IMP at either 10 or 50 μM for 24 h. After the treatment, IL-6 in culture medium was quantified using ELISA. + and *P < 0.01; * and **P < 0.01; ++ and **P < 0.01. B and C: RAW 264.7 cells were transfected with 200 nM ASMase or scrambled siRNA (control siRNA) for 24 h. After the transfection, ASMase knockdown by siRNA was confirmed using real-time PCR (B); the transfected cells were then treated with or without 1 ng/ml LPS, 100 μM PA, or both LPS and PA for 24 h, and IL-6 in culture medium was quantified using ELISA (C). + and *P < 0.01; ** and *P < 0.01; ++ and +P < 0.01. D and E: the effect of myriocin (serine palmitoyl-CoA transferase inhibitor) or fumonisin B1 (ceramide synthase inhibitor) on IL-6 secretion by RAW 264.7 cells treated with 1 ng/ml LPS, 100 μM PA, or both LPS and PA. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 1 ng/ml LPS, 100 μM PA, or both LPS and PA in the absence or presence of either 5 or 10 μM myriocin (D) or 250 μM fumonisin B1 (E) for 24 h. + and *P < 0.05. F: reduction of LPS and PA-stimulated nuclear p65 level by inhibitors of ceramide synthesis and sphingomyelin hydrolysis. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 1 ng/ml LPS and 100 μM PA in the absence or presence of 10 μM myriocin, 250 μM fumonisin B1, or 50 μM IMP for 24 h. After the treatment, nuclear protein was isolated and immunoblotting performed to detect p65, as described in materials and methods.
