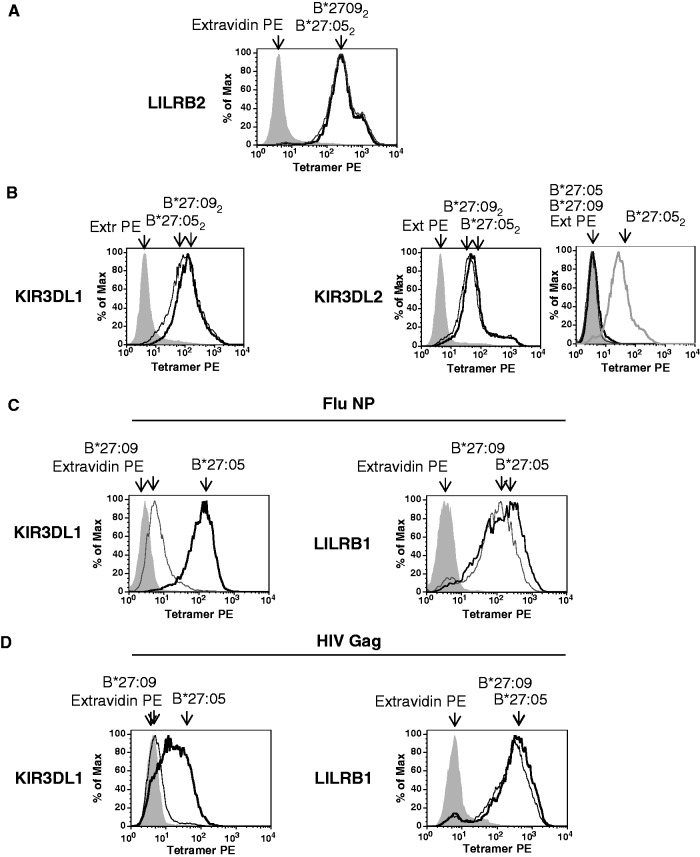
Fig. 4.
Similar binding of HLA-B*27:05 and HLA-B*27:09 dimers to KIR3DL1, KIR3DL2 and LILRB2. HLA-B*27:05 and HLA-B*27:09 heterodimers bind differently to KIR3DL1.
(A) Representative FACS staining of LILRB2-transduced Baf3 cells with HLAB*27:05 (B*27:052) and HLA-B*27:09 (B*27:092) dimer tetramers. Cells were stained with extravidin PE (EX PE) as a negative control stain. (B) Representative FACS staining of KIR3DL1- and KIR3DL2-transduced Baf3 cells with HLA-B*27:05 (B*27:052) and HLA-B*27:09 (B*27:092) heavy chain dimer tetramers. Representative staining of KIR3DL2-transduced Baf3 cells with HLA-B*27:05 (B*27:05) and HLA-B*27:09 heterodimer (B*27:09) tetramers. Staining with HLA-B*27:05 (B*27:052) heavy chain dimer tetramers (B272) is shown for comparison. Cells were stained with extravidin PE (EX PE) as a negative control stain. (C) Representative FACS staining of KIR3DL1- and LILRB1-transduced Baf3 cells with HLA-B*27:05 (B*27:05) and HLA-B*27:09 (B*27:09) heterodimer tetramers formed with the FluNP epitope. Cells were stained with extravidin PE (EX PE) as a negative control stain. (D) Representative FACS staining of KIR3DL1- and LILRB1-transduced Baf3 cells with HLA-B*27:05 (B*27:05) and HLA-B*27:09 (B*27:09) heterodimer tetramers formed with the HIV GAG epitope. Cells were stained with extravidin PE (EX PE) as a negative control stain.