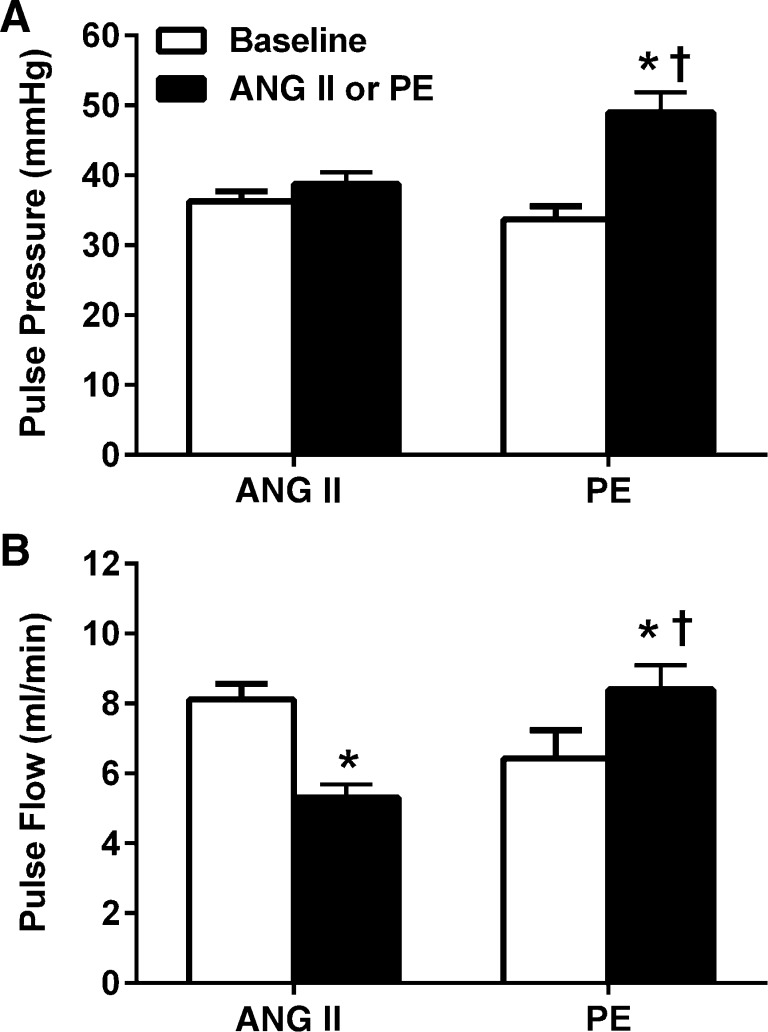
Fig. 3.
Pulse pressure and renal pulse flow at baseline and during chronic administration of ANG II (n = 11; 125 ng·kg−1·min−1) and PE (n = 8; 50 mg·kg−1·day−1) in conscious chronically instrumented rats. PE led to significant increases in both pulse pressure and renal pulse flow compared with baseline (P < 0.001) and ANG II-infused rats (P < 0.001). ANG II did not have any significant effects on pulse pressure but led to a significant reduction in pulse flow (P < 0.001 vs. baseline). Values are expressed as means ± SE. A: pulse pressure. B: renal pulse flow. *P < 0.05 vs. baseline. †P < 0.05 vs. ANG II-infused rats.