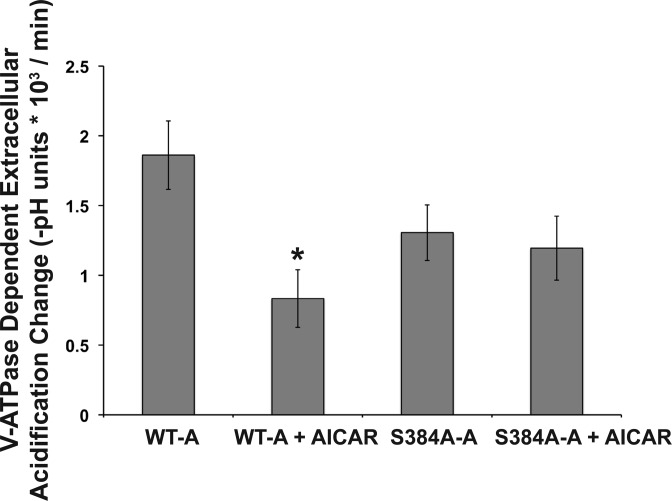
Fig. 6.
The Ser-384 A subunit mutant modulates bafilomycin-sensitive, V-ATPase-dependent extracellular acidification with AMPK activation in clone C cells. Clone C IC were transiently transfected with either the WT-A or S384A-A subunit. Twenty-four hours posttransfection, the cells were treated ± AICAR (2 mM) for 4 h and then pHo measurements were performed. The rate of extracellular acidification under each indicated condition was measured in a low-buffering-capacity solution before and after the addition of bafilomycin A1, a specific V-ATPase inhibitor (see materials and methods). The bafilomycin-sensitive rate of extracellular acidification [−(final buffer pH − initial buffer pH)/Δt] was obtained for cells incubated either with or without the AMPK activator AICAR (n = 5 for each transfection and treatment condition). Values are means ± SE. The transfection efficiency in each well was calculated as described in materials and methods, and no significant differences were observed across all conditions. *P < 0.01 relative to untreated cells transfected with the WT-A subunit.