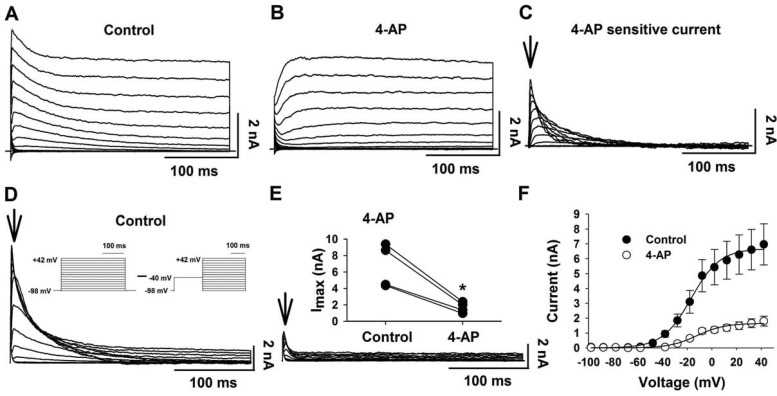
Fig. 4.
4-AP-sensitive outwardly rectifying K+ current in LC neurons. A: representative family of outwardly rectifying K+ currents elicited by command pulses (300-ms duration) from −116 to +34 mV with 10-mV increments; Vh = −96 mV. B: representative family of outwardly rectifying K+ currents elicited by the same command pulses in the presence of 4-AP (5 mM). C: representative family of 4-AP-sensitive outwardly rectifying K+ currents were obtained by subtracting the currents in B from those in A. Arrow shows time at which the current amplitude was quantified. D: representative family of A currents elicited by a different voltage-clamp protocol (inset) designed to identify the activation characteristics of the A current. TTX, Co2+, and TEA were added to the perfusate to eliminate Na+, Ca2+, and TEA-sensitive K+ currents. E: A currents in the presence of 4-AP (5 mM). Arrows show the times at which the current amplitudes were quantified. Inset: paired plot of A current amplitude in the absence (control) and the presence (4-AP) of 4-AP for 4 LC neurons. Note that 4-AP significantly inhibited Imax of the transient A current (*P < 0.05). F: activation I-V relationship for 4-AP-sensitive outwardly rectifying K+ current (n = 4) in the absence (●) and the presence (○) of 4-AP. The I–V plots were fit by Boltzmann curves. Symbols represent means ± SE.