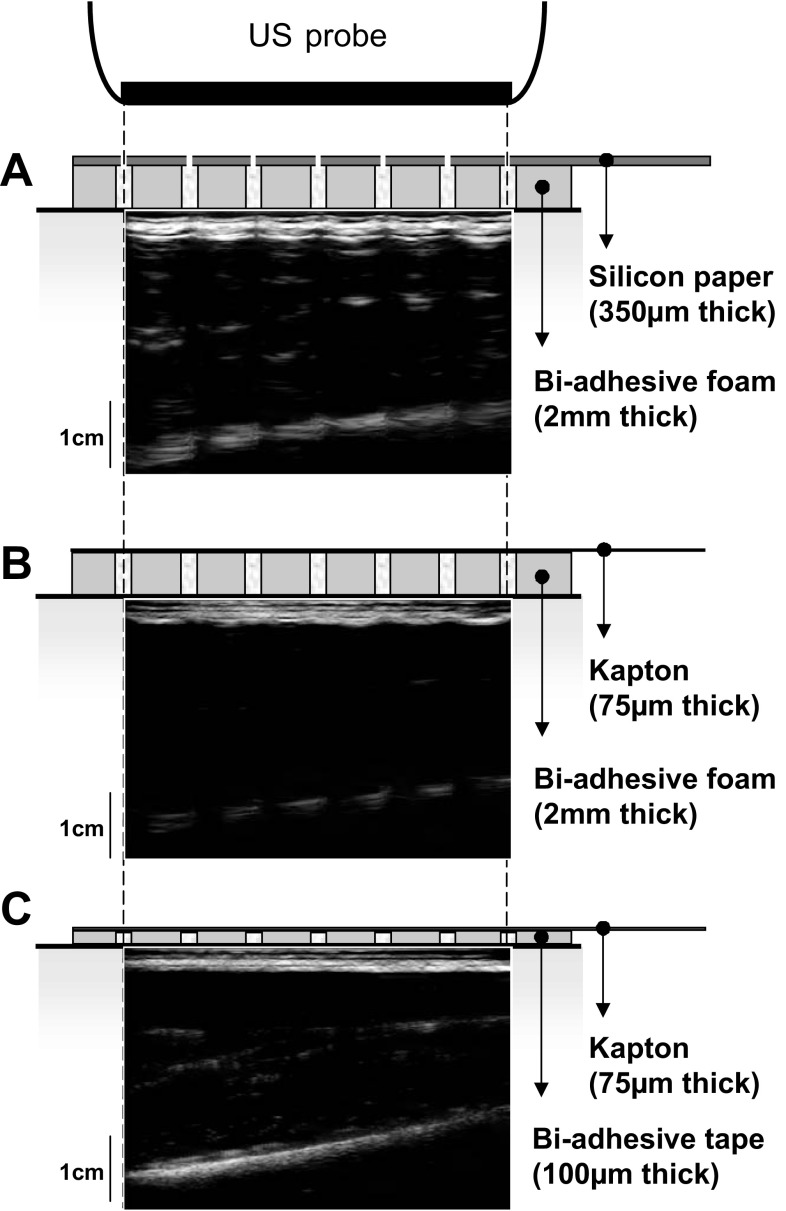
Fig. 1.
Ultrasound (US) images collected with different arrays of electrodes. US images collected with the US probe positioned over different configurations of electrode arrays reported in literature are shown. Arrays are constituted by a carrier material, which includes electrodes and their connections. Electrical contact between electrodes and skin is ensured by injecting conductive gel in the cavities of a biadhesive material interposed between arrays and skin. The three panels show US images collected with three different combinations of carrier and biadhesive material: silicon-coated paper and biadhesive foam (A), flexible printed circuit (kapton) fixed to the skin with biadhesive foam (B), and tape (C). Electrodes interposed between the US probe and the skin fully hinder the view of muscle tissue. A: for the configuration shown on top, conductive gel between electrodes and skin is injected through gaps present in the carrier material in correspondence of the electrodes. Note that, in this case, the US gel interposed between the US probe and skin would likely lead to short circuits between holes of neighboring electrodes.