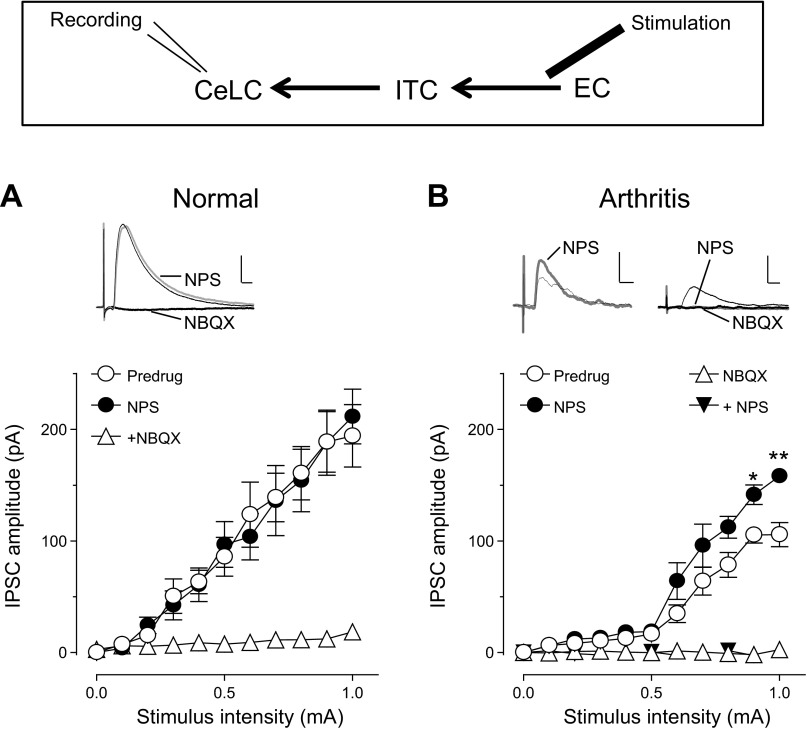
Fig. 4.
NPS increased feedforward inhibition of CeLC neurons in the pain model: whole cell patch-clamp recordings of CeLC neurons. Diagram shows stimulation and recording sites. A: in brain slices from normal rats NPS (1 μM) had no effect on IPSCs evoked by EC stimulation (n = 5 neurons; P > 0.05, F1,88 = 0.01, main effect of drug, 2-way ANOVA). NBQX (10 μM) inhibited IPSCs, suggesting that they were glutamate driven. B: in slices from arthritic rats NPS (1 μM) increased IPSCs significantly (n = 5; P < 0.0001, F1,88 = 24.76, main effect of drug, 2-way ANOVA). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Bonferroni posttests. In the presence of NBQX (10 μM), NPS had no significant effect (n = 6 neurons; P > 0.05, F1,110 = 2.71, main effect of drug, 2-way ANOVA). I/O relationships (means ± SE) were obtained by averaging peak amplitudes as a function of afferent fiber stimulus intensity. Insets: individual IPSCs (averages of 8–10) evoked with a stimulus intensity of 0.9 mA. Scale bars, 100 pA, 10 ms.