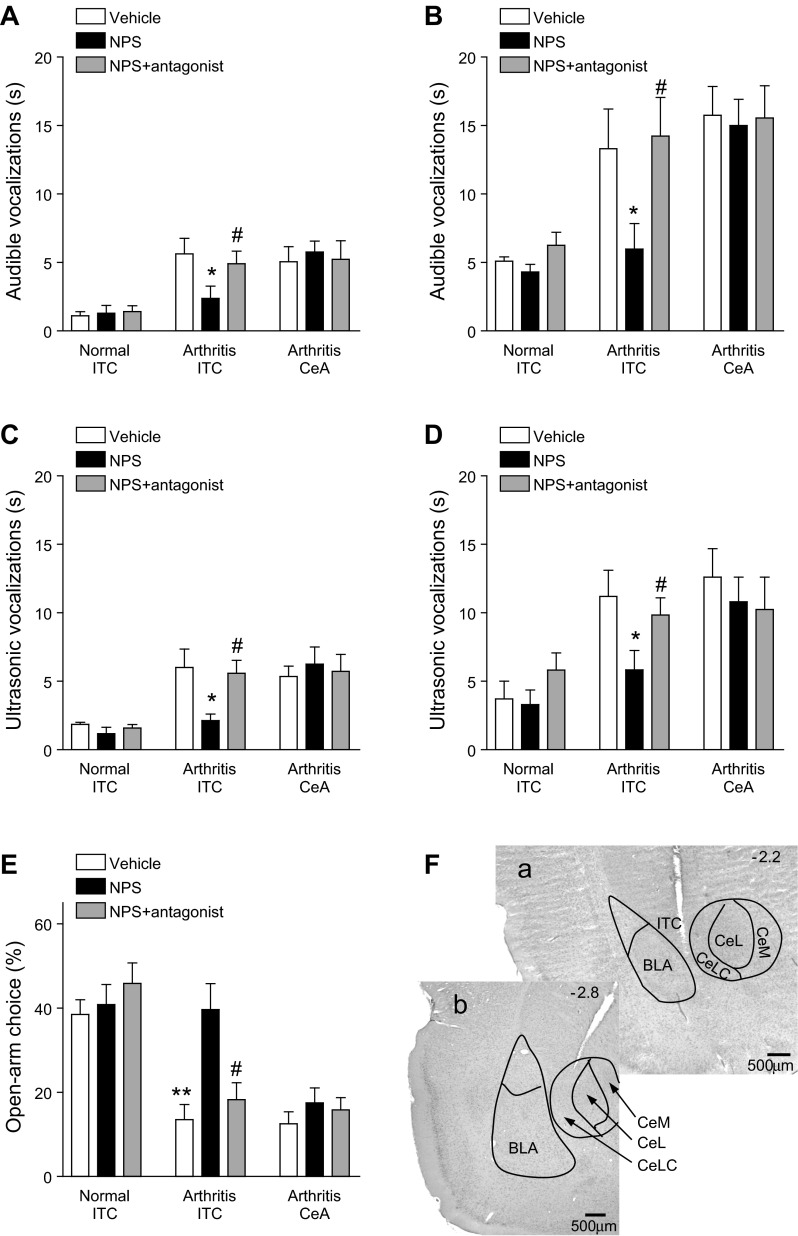
Fig. 9.
Administration of NPS into ITC, but not CeA, inhibited pain-related behaviors. Vehicle (ACSF), NPS (100 μM, concentration in microdialysis fiber) or NPS together with an NPSR antagonist ([d-Cys(tBu)5]NPS; 1 mM, concentration in microdialysis probe) were administered into ITC of normal or arthritic rats or into the CeA of arthritic rats (n = 5 in each of the 9 experimental groups). A and B: effect of these interventions on audible vocalizations evoked by innocuous (500 g/30 mm2; A) or noxious (2,000 g/30 mm2; B) mechanical compression of the knee (see methods). C and D: effect of interventions on ultrasonic vocalizations evoked by innocuous (C) or noxious (D) mechanical compression of the knee (see methods). E: effect of interventions on open-arm choice in the elevated plus maze test (open-arm entries expressed as % of total number of open-arm and closed-arm entries; see methods). Bar histograms show means ± SE. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ANOVA with Bonferroni posttests (compared with vehicle); #P < 0.05, ANOVA with Bonferroni posttests (compared with NPS). F: histological analysis shows examples of microdialysis probes positioned in the ITC (a) and CeLC (b) in coronal brain slices (2.2 and 2.8 mm caudal to bregma; see methods). CeL and CeM, lateral and medial division of CeA, respectively. The data show that NPS had inhibitory NPS receptor-mediated effects when administered into the ITC of arthritic rats.