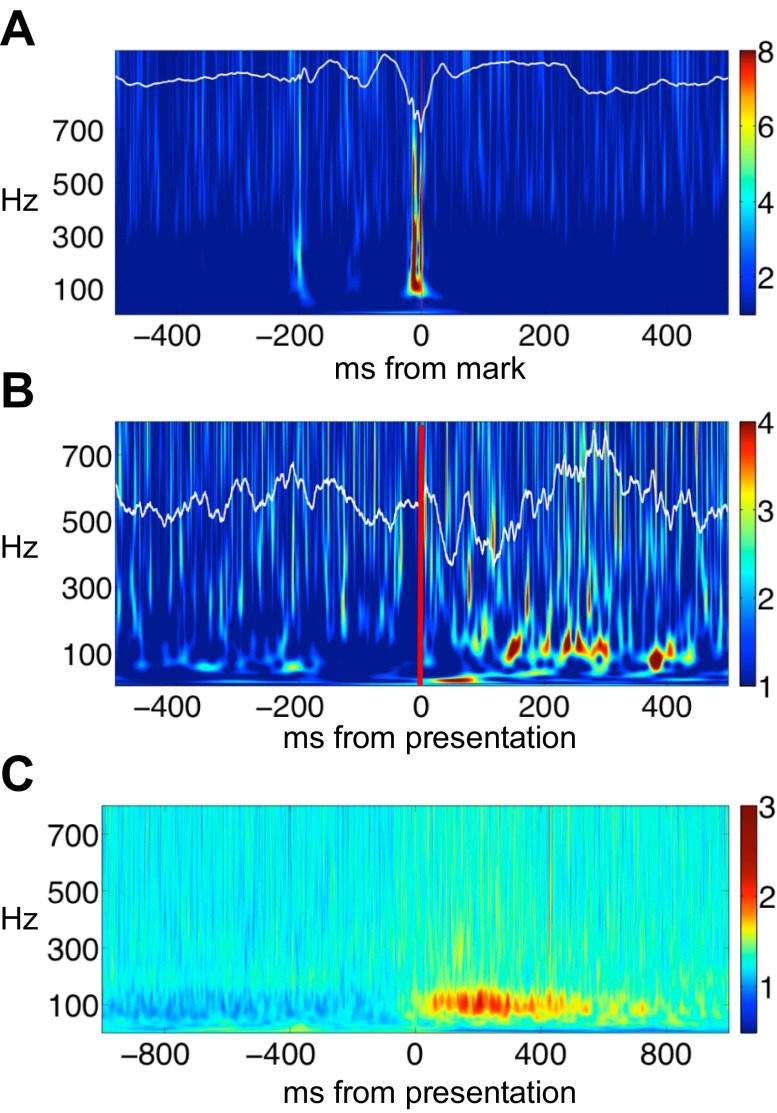
Fig. 1.
Pathologic high-frequency oscillations (pHFO) and physiologic high-frequency oscillations (nHFO) and task-induced gamma. A: pHFO identified in the time domain (white line tracing) superimposed on the corresponding Hilbert time-frequency spectrum. Time zero is the point marked on the raw record by the expert reviewer. Colorbar indicates Z-score of spectral amplitude in arbitrary units. Raw tracing and spectrogram demonstrate high-amplitude burst of HFO superimposed on a sharp wave. B: physiologic gamma oscillations induced by visual image presentation in a parahippocampal electrode from patient 4. Raw data in time domain (white line tracing) are superimposed on a single trial Hilbert time-frequency spectrum. Red line indicates onset of image presentation. Colorbar indicates Z-score of spectral amplitude in arbitrary units. Gamma oscillations appear as low amplitude, discrete modulations of the background frequencies during picture viewing. C: induced gamma oscillations appear on the averaged Hilbert time-frequency spectra between 100 and 400 ms after image presentation. Colorbar indicates Z-score of spectral amplitude in arbitrary units.