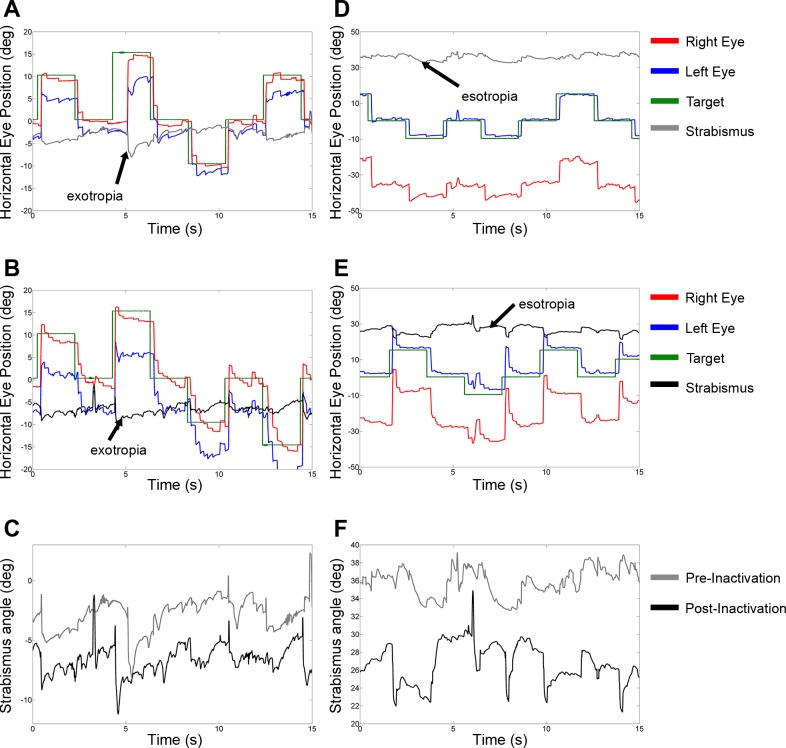
Fig. 4.
Example raw eye movement data showing effect of cFN inactivation on strabismus angle. Data in A–C are from the exotropic monkey (monkey S1, injection 3), and data in D–F are from the esotropic monkey (monkey S2, injection 5). A and D show preinactivation data; B and E show data after inactivation of the right cFN; C and F show a direct comparison of pre- and postinactivation strabismus angle (same data as in A and D and B and E). cFN inactivation induces an increase in exotropia (C; more negative strabismus angle—divergent change) and a decrease in esotropia (F; less positive strabismus angle—divergent change).