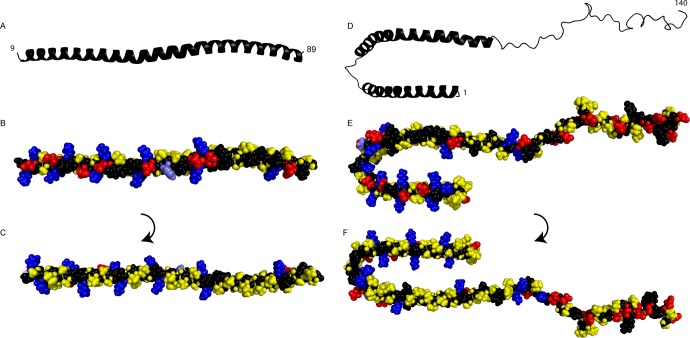
Figure 9.
(A–C) Structure of an α-synuclein fragment (residues 9–89) bound to 7:3 POPC/POPS small unilamellar vesicles30 (coordinates kindly provided by R. Langen). (D–F) Structure of α-synuclein bound to sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) micelles (Protein Data Bank entry 1XQ8).53 The broken N-terminal helix in panels D–F is a result of the nature of the supporting SDS micelles and is united into one extended helix upon bilayer binding.29,30,54 (A and D) Cartoon showing the helical N-terminus and the unstructured C-terminus. (B and E) Space filling model viewed from outside the vesicle or micelle with hydrophobic (yellow), cationic (blue), and anionic (red) residues. The titrating His50 is colored light blue for recognition. (C and F) Space filling model viewed from inside the vesicle or micelle with the same color coding.