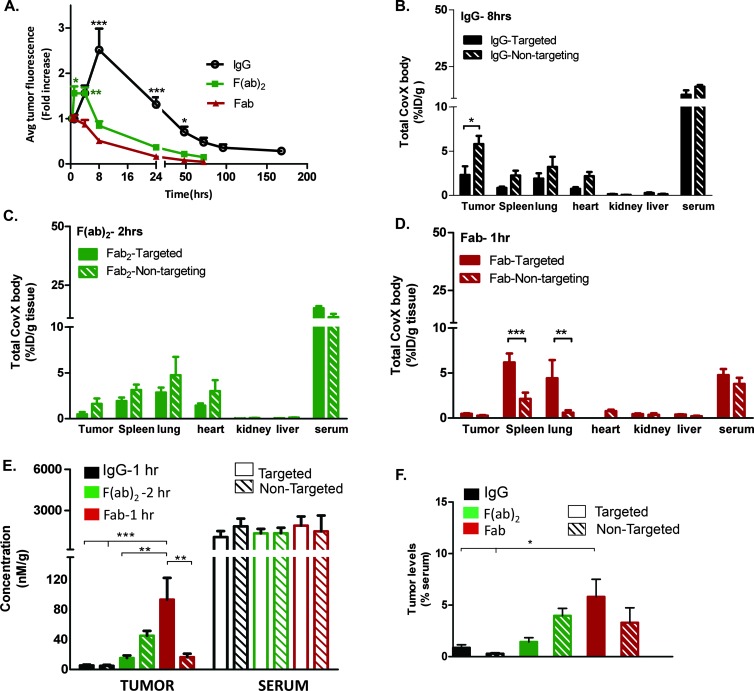
Figure 2.
Biodistribution studies. (A) Time-dependent tumor uptake of IgG, F(ab)2, and Fab. In vivo optical imaging of near infra-red (NIR)-conjugated constructs. Average signal intensities were quantified using regions of interest (ROIs) from the tumor sites. Data are presented as mean fold increase from initial image capture at 30 minutes ± SEM of eight mice (***P < .001, *P < .05; IgG vs both F(ab)2 and Fab accumulation, *P < .05 and **P < .01; F(ab)2 vs Fab accumulation by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). Tumor and normal tissue uptake of (B) IgG 8 hours post dose (*P < .05), (C) F(ab)2 2 hours post dose, and (D) Fab 1 hour post dose (***P < .001, **P < .01 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). (E) IgG, F(ab)2, and Fab tumor uptakes and serum levels compared at the early time points of 1 hour, 2 hours, and 1 hour, respectively. At this early time point with equivalent serum levels, the targeted Fab shows maximal accumulation levels compared to the F(ab)2 and IgG (***P < .001, **P < .01 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). (F) Tumor to serum levels further demonstrate that the Fab construct accumulation is significantly higher than the IgG accumulation (*P < .05 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test).