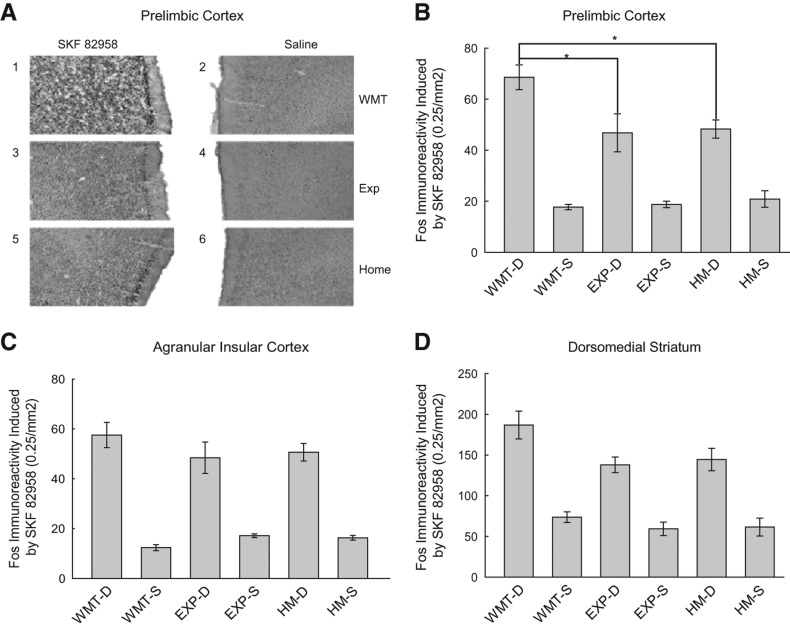
Figure 6.
Differences in c-Fos immunoreactive nuclei were observed across treatment groups. (A) Visualized c-Fos immunoreactivity in animals that had undergone working memory training (1), simple exposure to the apparatus (3), and those which remained in their home cages (5) 60 min after the administration of SKF82958. No differences were observed in either group of animals that received working memory training (2), exposure to the apparatus (4), or those which remained in the home cages (6) 60 min after the administration of saline. (B) Mean ± SEM number of c-Fos immunoreactive nuclei expressed in the prelimbic cortex of animals that have been segregated into groups which received working memory training (WMT), exposure to the apparatus (EXP), or remained in their home cages (HM). Groups labeled with “D” following their respective grouping received an administration of SKF82958 (1 mg/kg), whereas groups labeled with “S” received saline. Post hoc analysis revealed a significant difference in D1 agonist induced c-Fos immunoreactivity between animals that have undergone working memory training and animals that had been exposed to the apparatus for an equivalent amount of time (P < 0.05) as well as animals that remained in the home cages (P < 0.05). No significant differences in D1 agonist induced c-Fos immunoreactivity were observed between groups in the agranular insular cortex (C) or the dorsomedial striatum (D).