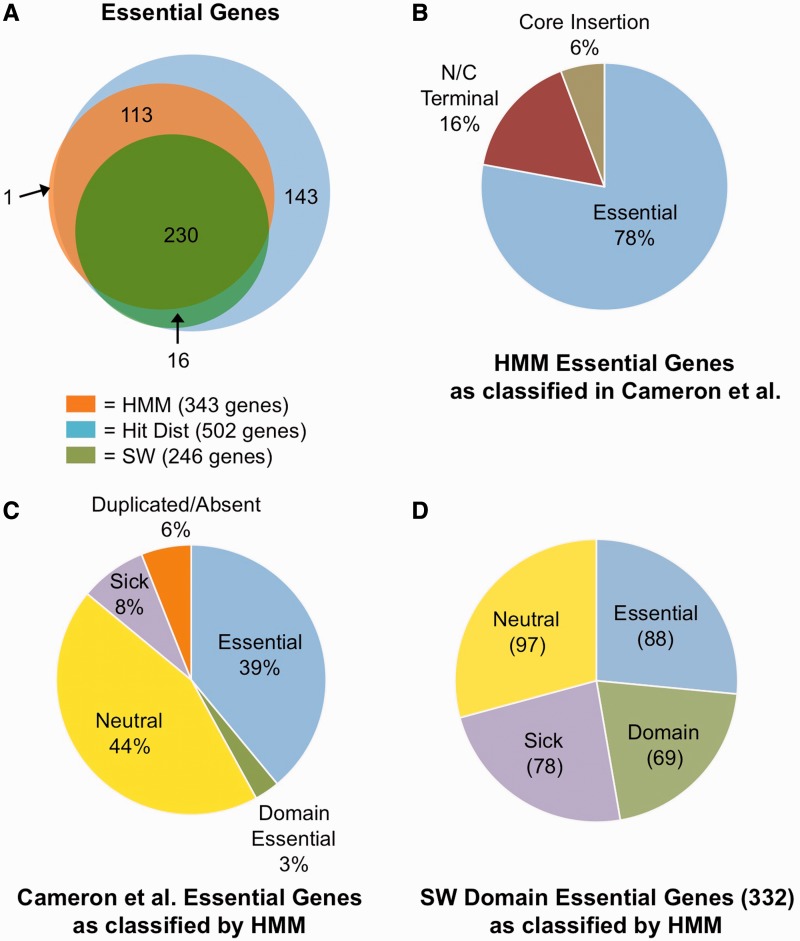
Figure 4.
Comparative analyses of V. cholerae gene classifications. (A) Overlap of V. cholerae essential genes predicted using various analytical approaches. The overlap between essential genes predicted using HMM and SW analyses (SW) are shown, as well as genes on the Hit Dist list, which have a significantly low (P < 0.01) fraction of TA sites disrupted. (B) The 343 V. cholerae genes classified as essential based on HMM analyses were compared with the assignments of Cameron et al. Genes without representative transposon mutants in the ordered transposon library were marked as ‘Essential’, while genes that contained a transposon insertion were separated into two groups: those with an insertion within 10% of the ends of the genes (‘N/C terminal’), or those that had insertions within the central 80% of the gene’s coding sequence (‘Core insertion’). (C) HMM-based gene classifications are shown for the 789 putative essential genes defined by Cameron et al (10). The frequency of duplicated loci and genes that are not in the V. cholerae C6706 genome (duplicate/absent), which were not classified by HMM, are also shown. (D) HMM classification of the 332 genes identified as domain essential using SW analysis.