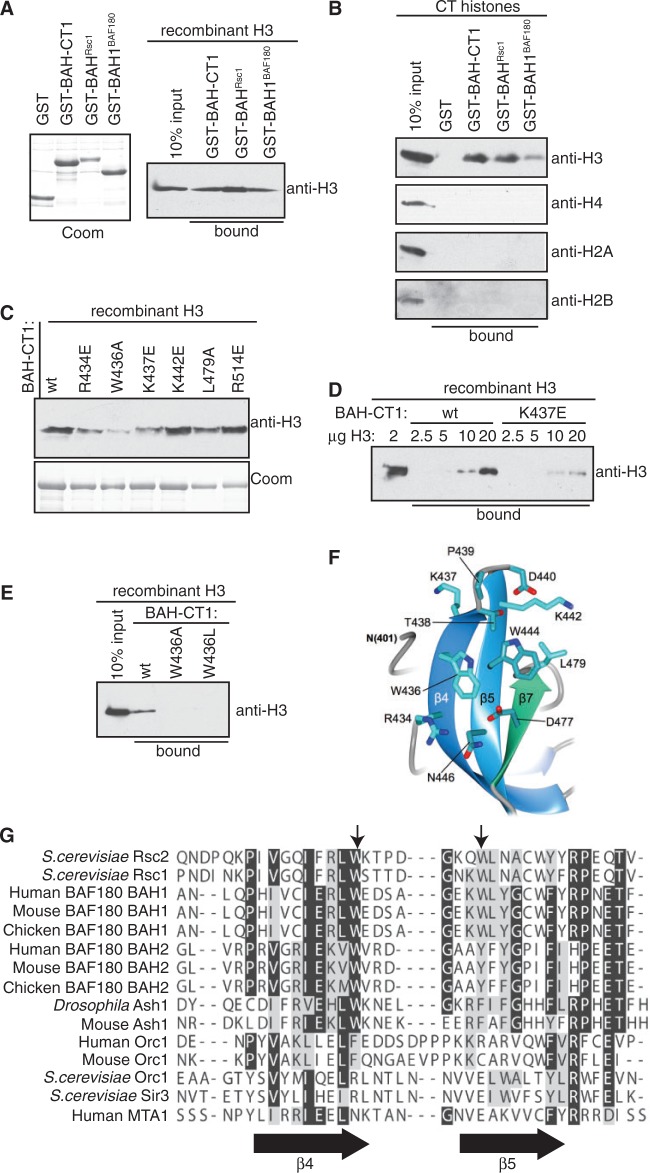
Figure 6.
A conserved motif on Rsc2 BAH mediates the interaction with H3. (A) Left panel: Coomassie stained gel of GST, GST-BAH domain from Rsc1 (GST-BAHRsc1) and GST-BAH1 from BAF180 (GST-BAH1BAF180). Right panel: GST pull-down assay using Rsc2 BAH-CT1 (GST-BAH-CT1), GST-BAHRsc1 or GST-BAH1BAF180 and recombinant histone H3. Bound protein was analyzed by western blotting using anti-H3. (B) Rsc2 GST-BAH-CT1, GST-BAHRsc1 and GST-BAH1BAF180 proteins were assayed for the ability to specifically interact with histone H3 from a mixture of calf thymus core histones in pull-down assays. Bound protein was analyzed by western blotting using antibodies specific for each of the four core histones. (C) A panel of mutant Rsc2 GST-BAH-CT1 proteins was assayed for the ability to interact with histone H3 in pull-down assays. Bound protein was analyzed by western blotting using anti-H3 antibody. Coomassie stained gel of the GST-BAH-CT1 proteins used in the pull-down assays (bottom panel). (D) GST-BAH-CT1 or GST-BAH-CT1-K437E was used in pull-down assays containing the indicated amount of recombinant H3 and bound protein was analysed by western blotting using anti-H3. (E) Molecular details of the β4–β5 connecting loop of Rsc2 BAH-CT1 showing the positions of Trp436, Lys437 and Trp444. (F) GST pull-down assay using wt, W436A and W436L GST-BAH-CT1 constructs. Bound protein was analyzed by western blotting using anti-H3. (G) Sequence alignment of the region of the BAH domain encompassing β4, β5 (indicated by arrows below the alignment) and the connecting loop. The positions of Trp436 and Trp444 in Rsc2 are indicated by arrows above the alignment.