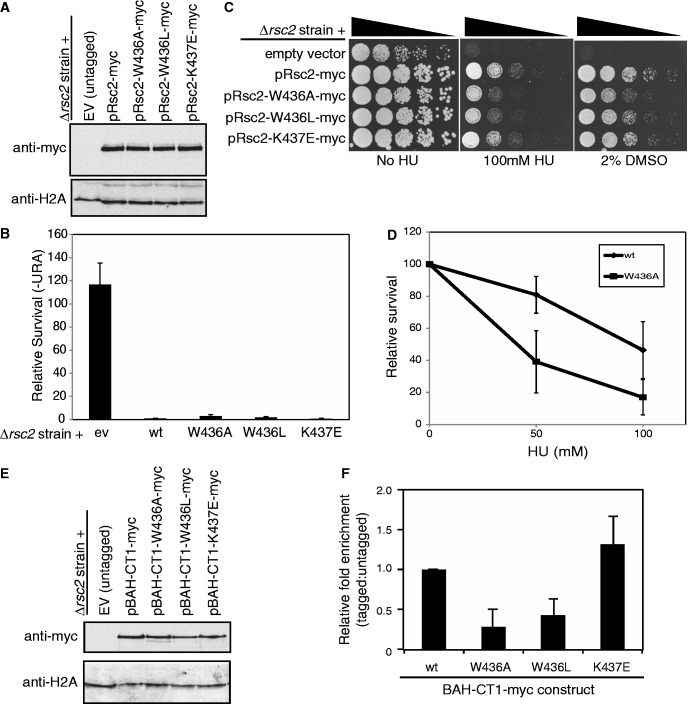
Figure 7.
Mutation of the conserved motif in the Rsc2 BAH domain that is important for H3 binding in vitro disrupts some Rsc2 functions in vivo. (A) Western blot analysis of whole cell lysates prepared from rsc2 null strains carrying empty vector or expression constructs with full-length Myc-tagged Rsc2 (wt, W436A, W436L or K437E mutant) using anti-myc (top panel) or anti-H2A (bottom panel) as a loading control. (B) Silencing was monitored as in Figure 1B using the rsc2 null strain carrying either empty vector, wt Rsc2 or mutant Rsc2 constructs, and the data are represented as the mean ± 1 SD of at least three independent experiments. (C) The W436A and W436L mutant Rsc2 proteins are unable to fully complement the hypersensitivity of an rsc2 null strain. Serial dilutions of mid-log cultures were plated onto media containing the indicated drug and incubated for 2–3 days at 30°C before imaging. (D) Survival of the W436A mutant strain compared with wt Rsc2. Three independent cultures of each strain were grown and plated onto media containing the indicated amount of HU. Survival was calculated relative to media lacking HU and the data are shown ± 1 SD. (E) Western blot analysis of whole cell lysates prepared from rsc2 null strains carrying either empty vector or overexpression BAH-CT1-myc constructs as indicated using anti-myc (top panel) or anti-H2A (bottom panel) as a loading control. (F) W436A and W436L mutations in Rsc2 BAH-CT1 impair chromatin association in vivo. ChIP assays examining enrichment of Myc-tagged overexpressed BAH-CT1 relative to the untagged control at the 18S region of the rDNA. Data shown are the mean enrichment of at least three independent experiments ± 1 SD.