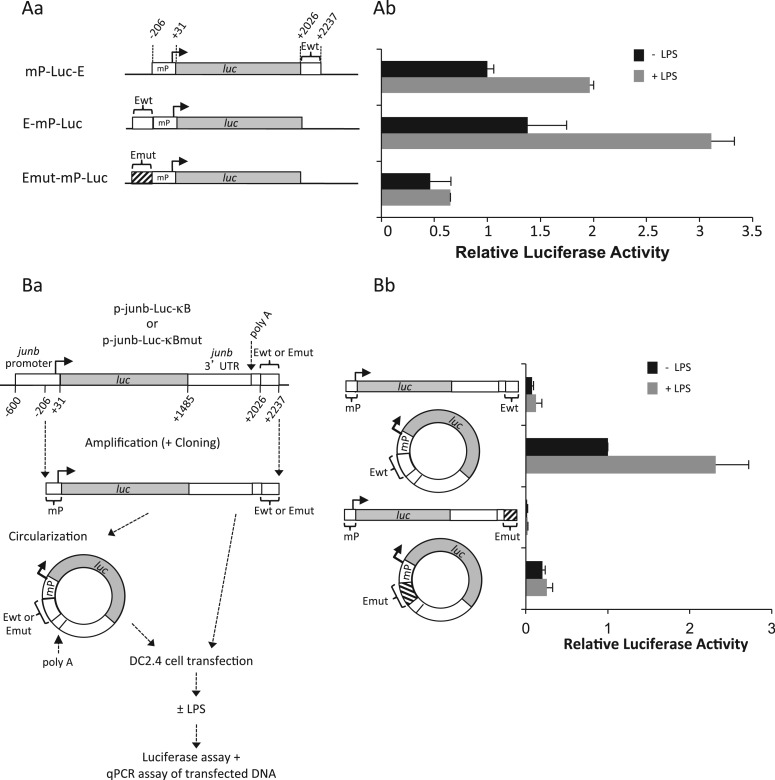
Figure 8.
Stronger transcriptional activity in response to LPS stimulation upon forced proximity of junb promoter and enhancer regions. (A) Transfection of mP-luc-E, E-mP-luc and Emut-mP-luc plasmids in DC2.4 cells. junb minimal promoter (mP), wild-type E domain and E-domain mutated on the NF-κB-responsive sites were cloned upstream or downstream of the luciferase gene (luc) of the pGL3 reporter plasmid as indicated in Aa. mP corresponds to positions −206/+31 in mouse junb and E to positions +2022/+2237. DC2.4 was transfected, stimulated and processed for luciferase assay as in Figure 2G. Plasmids were cleaved with the Ase I restriction enzyme that cuts on both sides of the mP-luc-E, E-mP-luc and Emut-mP-luc fragments to avoid bias linked to the circular nature of plasmids. The presented data are the results of three independent experiments (Ab). (B) Transfection of linear and circular fragments bearing chimeric luc/junb genes. DNA fragments spanning the minimal junb promoter (starting at position −206) to the end of the E domain (position 2237) were purified from the p-junb-Luc-κB- and the p-junb-Luc-κBmut reporter plasmids used in Figure 2G. They were then circularized using the T4 DNA ligase as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section. DC2.4 cells were then parallely transfected with the linear and circular isoforms of these fragments and LPS-stimulated as described in Ba before assays of both luciferase activity and luciferase DNA in cell lysates. The latter DNA assays showed comparable amounts of the DNA isoforms at the end of the experiments. The results of luciferase assay after normalization of data are presented in Bb. They correspond to four independent experiments. Details of experimental procedures are given in ‘Materials and Methods’ section.