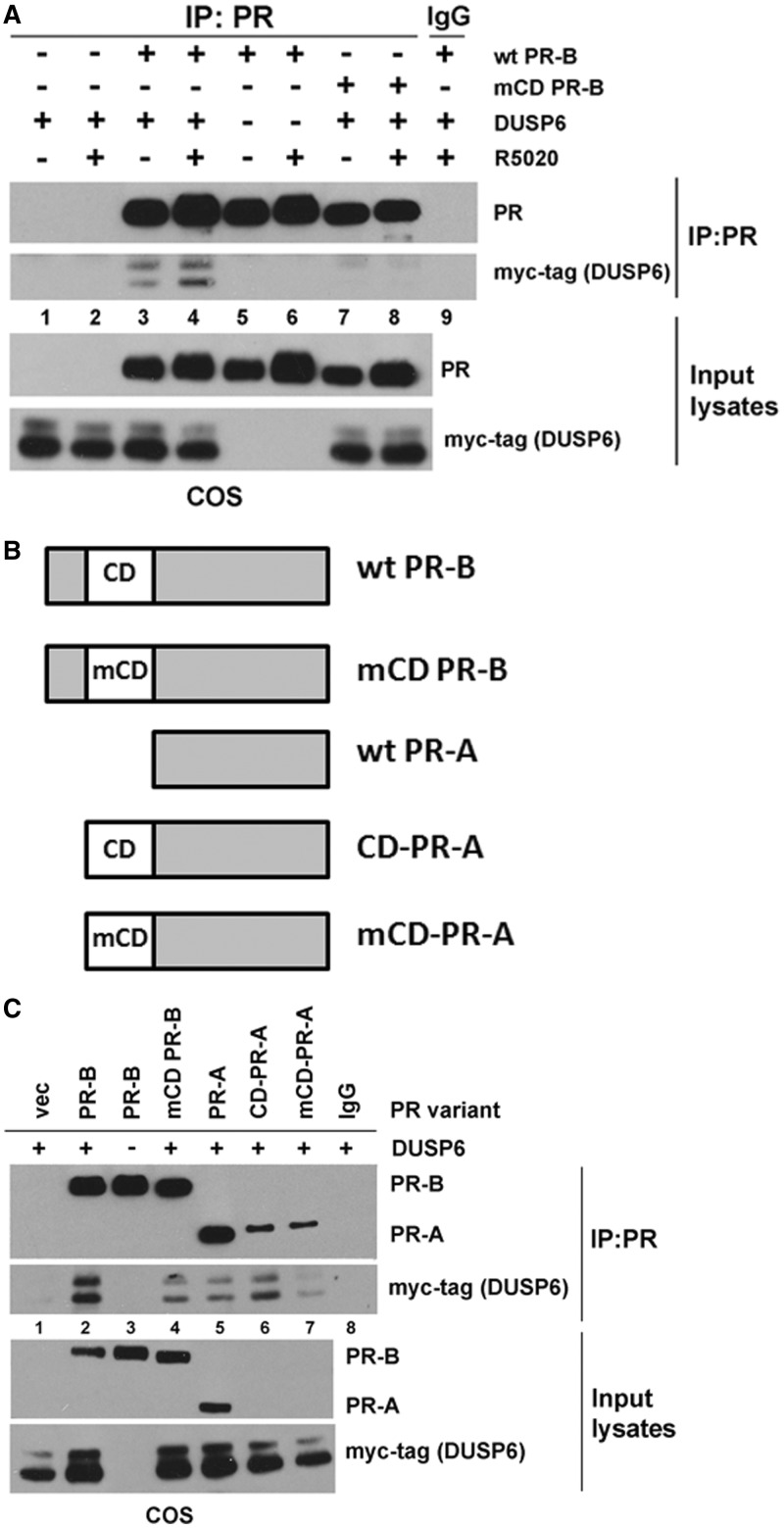
Figure 4.
PR-B interacts with DUSP6 through the CD domain. (A) CD-domain dependent interaction between PR-B and DUSP6. COS cells were transiently transfected with wt PR-B, mCD PR-B or vector alone, as well as myc-tagged DUSP6 (or vector). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were starved for 18 h in serum-free media and then treated with 10 nM R5020 or EtOH for 60 min. Lysates were IP'd with PR antibody or mouse IgG (control). IP lysates or input lysates (25 µg not subjected to immunoprecipitation) were analyzed via western blotting using PR-B or myc-tag (to detect myc-tagged DUSP6) antibodies. Myc-tagged DUSP6 resolves as a doublet by western blotting due to alternate translational start sites. (B) Schematic representing wt and mutant PR-B constructs. The CD domain in wt PR-B (top) was mutated to create mCD PR-B (as described above). PR-A lacks a BUS region where the CD domain is located. A synthetic wt or mutant CD domain was fused to the N-terminus of wt PR-A to create CD-PR-A or mCD-PR-A, respectively. (C) CD domain-mediated interaction between PR-B and DUSP6. COS cells were transiently transfected with the indicated PR constructs or vector alone, as well as myc-tagged DUSP6 (or vector). CoIP and western blotting were performed as described in (A).