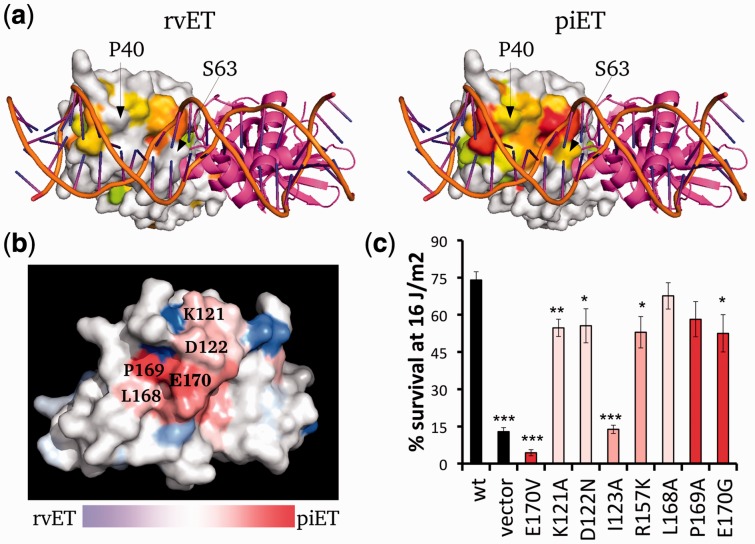
Fig. 4.
The piET algorithm provides better biological understanding of LexA. (a) The piET algorithm identifies the DNA binding site of LexA better when compared with the rvET analysis (PDBID 3jsp). The residues deemed to be in the top 30% are colored based on evolutionary importance where red is considered the most important. (b) piET identifies a novel cluster of residues. The rvET–piET difference scale is calculated by taking the normalized difference of the rank percentiles. Residues are marked red (piET) or blue (rvET) when the residue is significantly more important to respective method. (c) Mutations at this new LexA site disrupt DNA damage survival. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001