Figure 4. Overexpression of miR-382 is sufficient to inhibit alcohol-induced up-regulation of DRD1 and DeltaFosB in rat NAc: *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001, ##p < 0.001, Student's t-test.
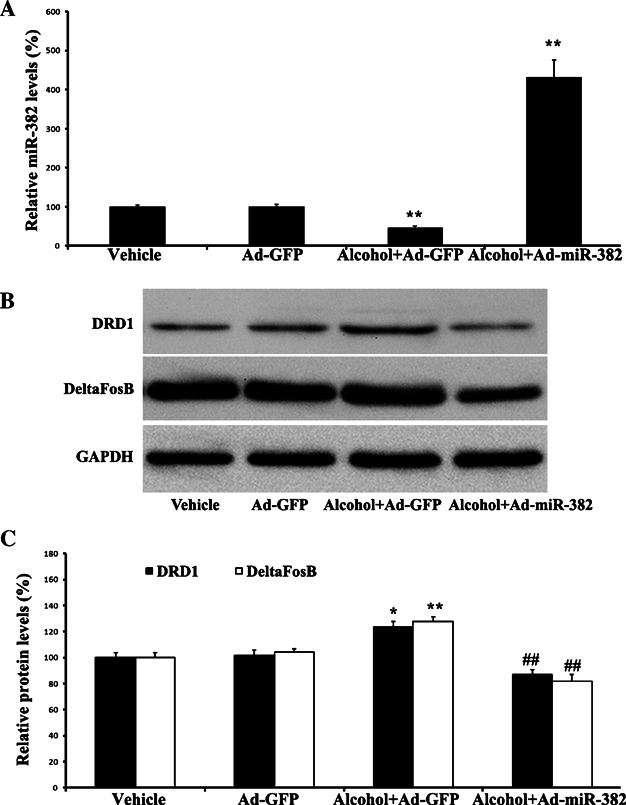
Source data is available for this figure in the Supporting Information. At 3 days before alcohol administration, 4 µl of vehicle, Ad-GFP or Ad-miR-382 (1 × 109 pfu/ml) was infused into the NAc of rats. Then, the animals were divided into the following groups: Vehicle-treated rats without alcohol administration (Vehicle); Ad-GFP-treated rats without alcohol administration (Ad-GFP); Ad-GFP-treated rats with alcohol administration (Alcohol + Ad-GFP) and Ad-miR-382-treated rats with alcohol administration (Alcohol + Ad-miR-382). Severn days later, the rat NAc were isolated.
- The successful modulation of miR-382 expression by Ad-miR-382. Alcohol decreased the expression of miR-382 in rat NAc (p = 0.00076). Values are mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments (n = 3), Alcohol + Ad-GFP compared with that in Ad-GFP control. Ad-miR-382 increased the expression of miR-382 in NAc of rats with alcohol administration (p = 0.00079). Values are mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments (n = 3), Alcohol + Ad-miR-382 compared with that in Alcohol + Ad-GFP control.
- Representative Western blots in rat NAc from different treatments.
- Downregulation of DRD1 and DeltaFosB via overexpression of miR-382 in NAc. Alcohol administration increased the expression of DRD1 (**p = 0.00616) and DeltaFosB (**p = 0.00087). Values are mean ± SEM from 5 independent experiments (n = 5), Alcohol + Ad-GFP compared with that in Ad-GFP control. Overexpression of miR-382 via Ad-miR-382 prevented alcohol-induced up-regulation of DRD1 (##p = 0.0002) and DeltaFosB (##p = 0.00012) in rat NAc. Values are mean ± SEM from 5 independent experiments (n = 5), Alcohol + Ad-miR-382 compared with that in Alcohol + Ad-GFP control.
