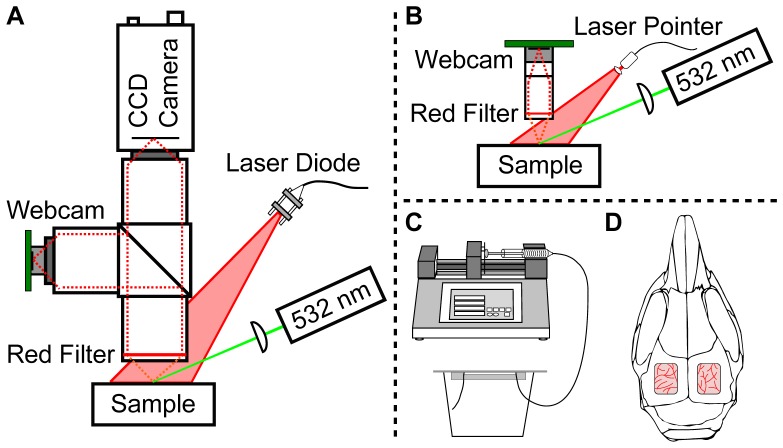
Fig. 1.
(A) Schematic of the two-camera setup for simultaneous laser speckle imaging with a CCD camera and a webcam using traditional optics and illumination components. A 50-50 beamsplitter separates the light between the two imaging arms. (B) Schematic of the low-cost, compact laser speckle imaging system, where the lenses are inexpensive aspheres and the illumination is a laser pointer. In both (A) and (B), the 532 nm laser is only used for the animal study. (C) and (D) illustrate the two different samples assessed in this study. (C) A microfluidic flow phantom is used for in vitro validation and different flow levels are controlled using a syringe pump. (D) In vivo validation is performed using a mouse prepared with bi-lateral cranial windows for assessment of setup (A) and (B), respectively.