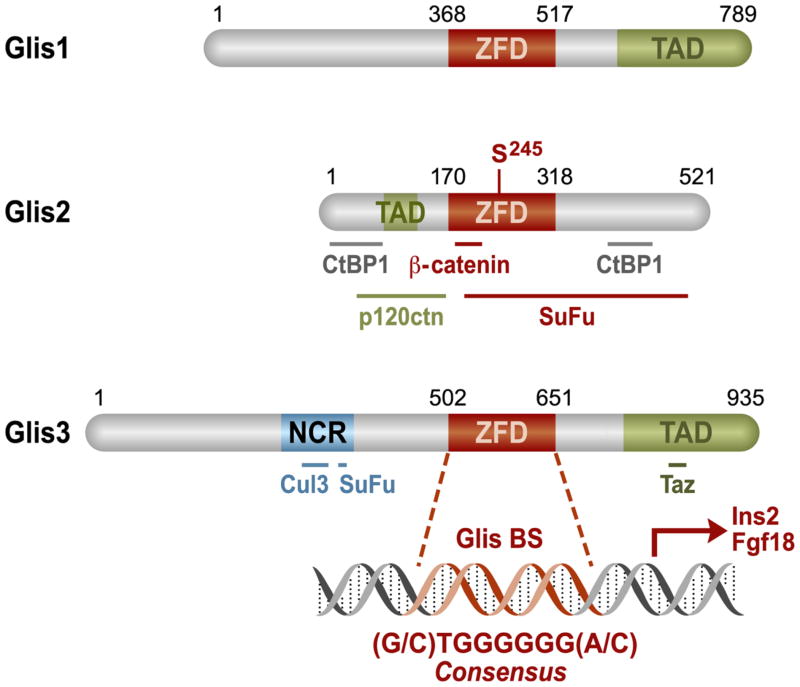
Figure 1. Schematic representation of Glis1-3 protein structure.
The primary structure of Glis proteins and their identified domains are shown (ZFD = zinc finger domain; TAD = transactivation domain; NCR = N-terminal conserved region that is shared with GLI proteins). Bold lines represent regions within Glis proteins required for their interaction with C-terminal binding protein 1 (CtBP1); p120 catenin (p120ctn), Suppressor of Fused (SuFu), Cullin 3 (Cul3), and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (Taz) as indicated. The potential phosphorylation site, Serine245, is specified in Glis2. Numbers indicate the amino acid position.