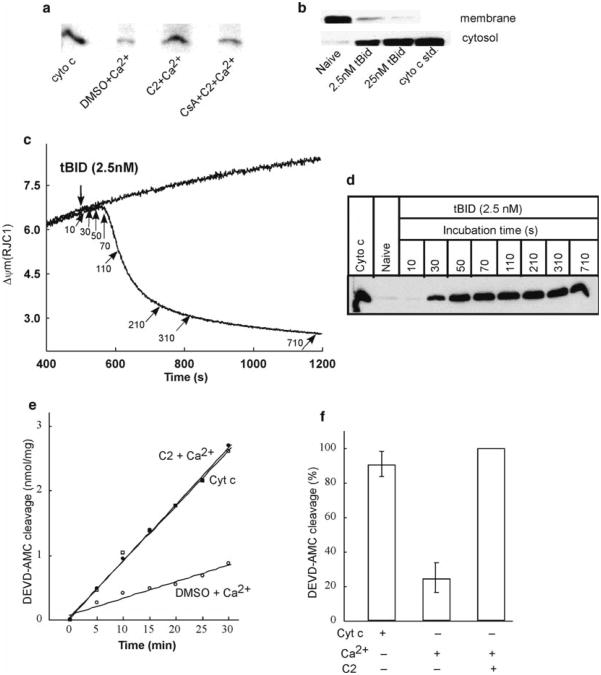
Fig. 4.
Release of cytochrome c and activation of caspases after ΔΨm loss in permeabilized HepG2 cells. Upper panel shows the immunoblots of cytochrome c in cytosolic and membrane fractions generated after the measurements of ΔΨm in permeabilized cells. Cytosolic samples generated from the experiments described in Fig. 2a, b shows higher amount of cytochrome c in presence of C2 + Ca2+ compared to that of C2 + Ca2+ + CsA reflecting PTP opening (a). Membrane and cytosolic samples generated after ΔΨm measurements in presence of two different concentrations of tBid shows dose-dependent release of cytochrome c in cytosol from the mitochondria (b). Middle panel shows that tBid-induced ΔΨm loss is closely coupled to cytochrome c release. ΔΨm was monitored in permeabilized cells treated with 2.5 nM tBid in the presence of succinate, ATP, ATP regenerating system, and oligomycin. Arrows indicate the time points at which cytosolic samples were generated by rapid filtration of the cells (c). Panel (d) shows time course of tBid-induced cytochrome c release as determined by Western blotting of the cytosolic samples. Lower panel shows caspase activation associated with Ca2+ -induced opening of PTP. Fluorometric assay of DEVD–AMC cleavage in cytosol extracts prepared at the end of measurements of ΔΨm (see Fig. 2a) was carried out. Data in (e) shows the increase of Caspase 3 activity in presence of C2 + Ca2+ compared to DMSO control. Addition of exogenous cytochrome c in DMSO control cytosol increased its activity of Caspase 3 at the level of C2 + Ca2+ condition indicate that activation of Caspase 3 is downstream to the cytochrome c release. Data in (f) shows the DEVD-AMC cleavage normalized to the activity obtained with C2 + Ca2+. Panels (a) and (e) are reproduced from (7) with modification with permission from The EMBO Journal, whereas panels (c) and (d) from (20) with modification with permission from The Journal of Biological Chemistry