Fig. 1.
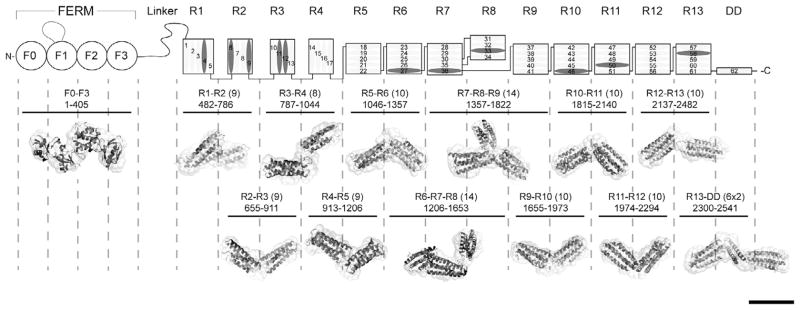
Domain structure of talin1 and SAXS analysis of talin1 polypeptides. The N-terminal FERM domain (residues 1–400), which is atypical in that it comprises 4 domains F0–F3 and a long unstructured loop in F1, is coupled to a flexible rod (residues 482–2541) by an unstructured linker. The 62 α-helices of the talin1 rod are organized into 13 amphipathic helical bundles (R1–R13) terminating with the C-terminal dimerization helix (DD). The rod comprises nine 5-helix bundles, and three of the four 4-helix bundles are arranged in tandem close to the N-terminus of the rod. Helices that support vinculin binding are in dark grey. The residue numbers of each polypeptide used in the study are shown (number of helices in brackets). The Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) envelope reconstruction of overlapping double and triple talin rod domain polypeptides is shown below the schematic diagram of talin1. The atomic resolution structures of the individual talin domains are fitted into the SAXS envelopes. The SAXS envelope of the talin FERM domain is also shown. Bar represents 5 nm.
