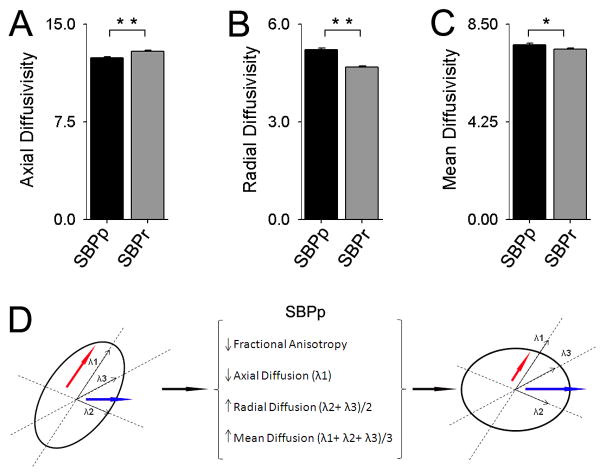
Figure 3. Diffusivity properties for white matter tracts where FA was lower in SBPp.
Diffusivity differences were examined for the grp-FA mask at visit 1: (A) Axial diffusion was decreased in SBPp (t22 = −4.68, p< 0.01); (B) Radial diffusion increased in SBPp (t22 = 7.39, p < 0.01); and (C) Mean diffusion increased in SBPp (t22 = 2.61, p= 0.016), demonstrating that the increase in radial diffusion outweighs the decrease in axial diffusion. All three bargraphs are in units 10−4 × mm2/second. (D) Schematic representing the relationship between fractional anisotropy and component diffusion parameters. Axial (red arrow) and Radial (blue arrow) Diffusions are shown in an ellipsoid representing the tensor for a given white matter voxel. For regions showing reduced FA, SBPp patients have reduced axial and increased radial diffusion (increasing MD), thus making the ellipsoid more spherical, resulting in reduced FA.