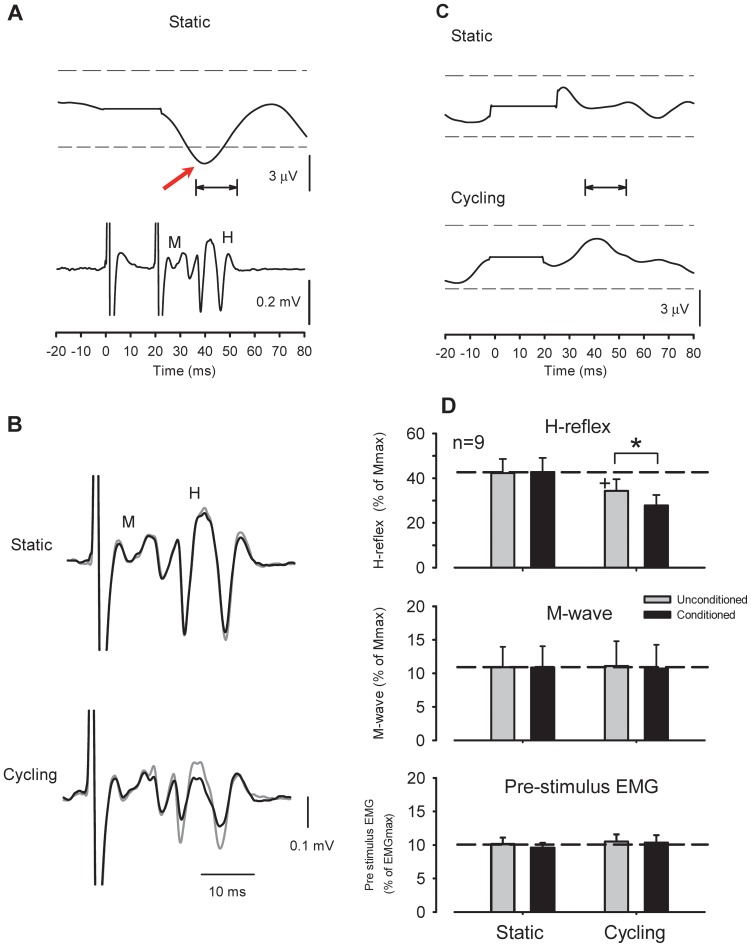
Figure 4. Effect of radial nerve conditioning on flexor carpi radialis (FCR) H-reflex amplitudes during leg cycling.
(A) Rectified and averaged FCR EMG and H-reflex waveforms following radial nerve stimulation [1.0× motor threshold (MT)] obtained from a single subject. Time zero on the x-axis is onset of conditioning stimulation. Please note that the EMG reflex responses (upper traces) had latencies that corresponded with the H-reflex (lower traces) during the conditioning-test interval. Horizontal arrows show analysis range for assessing ongoing FCR EMG. The arrow shows the suppressive response in the rectified EMG. (B) Conditioning effect of weak radial nerve stimulation (0.6×MT) on FCR H-reflex amplitude during static activation (gray traces) and leg cycling (black traces). (C) EMG responses following weak radial nerve stimulation (0.6×MT) during static and cycling tasks. Non-significant EMG responses were within 2 standard deviations (SD) of the pre-stimulus EMG levels. Broken lines in each panel represent a 2 SD band around the mean pre-stimulus EMG. Note that the stimulus artifact was replaced by the mean of the pre-stimulus EMG. Data in Figures 4A, B, and C were obtained from the same subject. (D) Grand means (± SEM) of H-reflex amplitudes (upper panel), M-waves (middle panel), and pre-stimulus EMG (lower panel) in the FCR muscle during radial nerve conditioning obtained from 9 subjects. * p<0.01 significantly different from the unconditioned values for each task. +p<0.01 significantly different from the unconditioned static value.