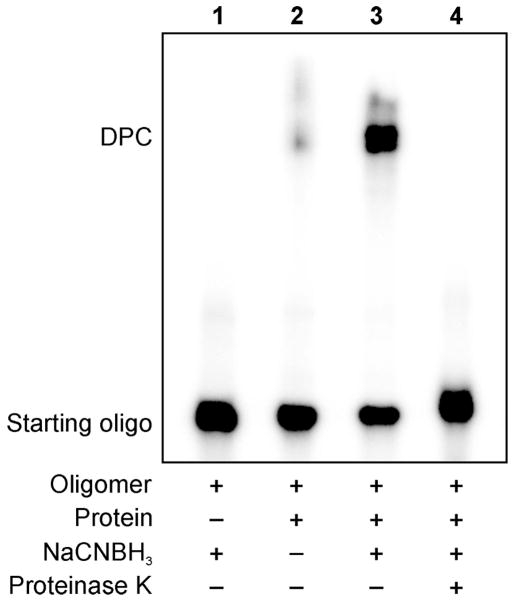
Figure 1.
Denaturing SDS-PAGE analysis of DNA-protein cross-links generated by reductive amination reaction (Scheme 2) between E. coli AlkB protein and aldehyde-containing DNA 20-mer, 5′-G TCA CTG GTA DHP-deaza-dG CA AGC ATT G-3′. DNA and DNA-protein conjugation products were visualized by 32P-end labeling. The formation of covalent DPC is revealed as a low mobility band on the gel. Lane 1: aldehyde containing oligonucleotide in the presence of a reducing agent (negative control); Lane 2: aldehyde containing oligonucleotide and AlkB protein in the absence of a reducing agent; Lane 3: reaction mixture of aldehyde containing oligonucleotide and the protein in the presence of a reducing agent; Lane 4: reaction mixture from lane 3 subjected to proteinase K digestion.