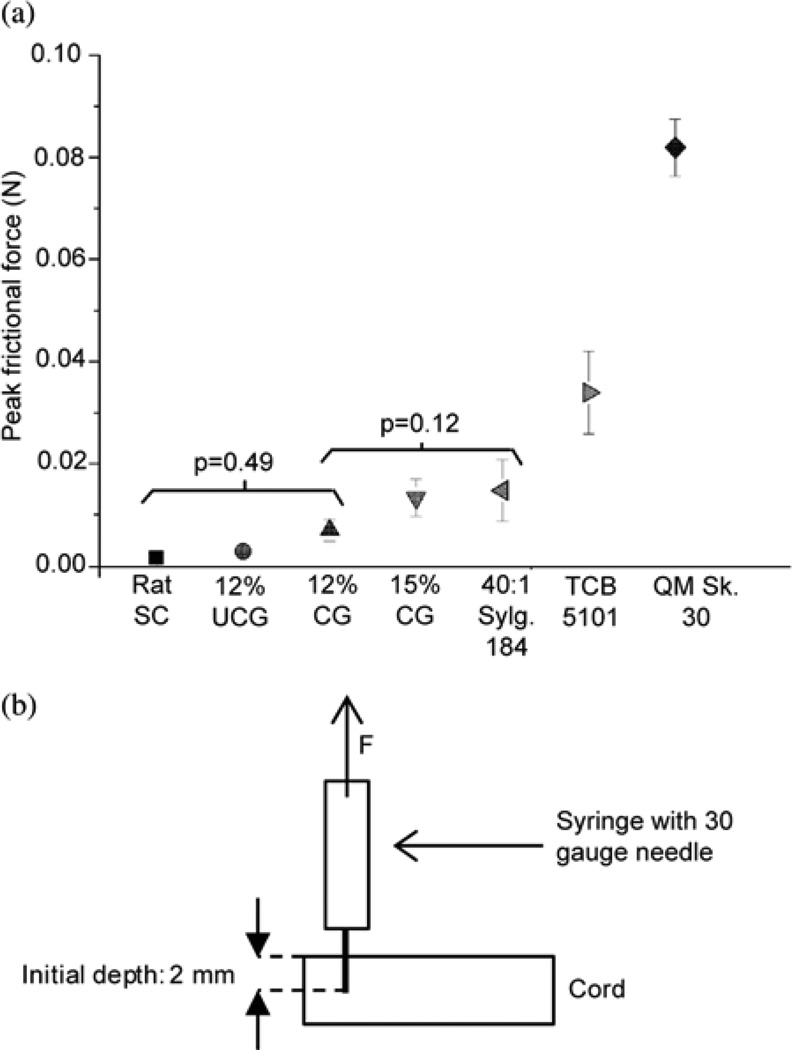
Fig. 5.
(a) Average peak interfacial frictional forces of the candidate surrogate spinal cord materials. Average ± standard deviation of peak interfacial frictional forces required to withdraw a 30 gauge needle from candidate silicone, crosslinked gelatin (CG), and uncrosslinked gelatin (UCG) surrogate spinal cords, as well as rat spinal cords. For each test, the needle was inserted to 2 mm and withdrawn for 2 mm. The results of the ANOVA and Tukey HSD post hoc analyses are shown along with the p-values. The brackets denote the groups within which differences were not statistically significant. The forces required to withdraw the needle from the 12 wt% gelatin cords were not significantly different from those required to withdraw the needle from the rat cords. (b) Diagram of the setup utilized to characterize the peak frictional force required to withdraw the needle.