Figure 1.
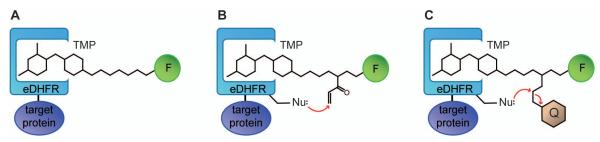
Cartoon of TMP-tags. (A) Non-covalent TMP-tag is based on the high-affinity interaction between E. coli dihydrofolatereductase (eDHFR) and the antibiotic trimethoprim (TMP). The target protein (purple) is tagged with eDHFR (blue) and then labeled with a cell-permeable TMP-fluorophore (F) heterodimer. (B) The TMP-tag is rendered covalent by installing a nucleophilic amino acid near the binding pocket to react with a latent electrophile (acrylamide) when TMP binds to eDHFR. (C) The fluorogenic TMP-tag centers a TMP-quencher (Q) –fluorophore (F) heterotrimer. When TMP binds to eDHFR, the nucleophilic amino acid near the binding pocket initiated a proximity-induced SN2 reaction that cleaves the electrophile attached to the quencher and thus switches on the fluorophore.
