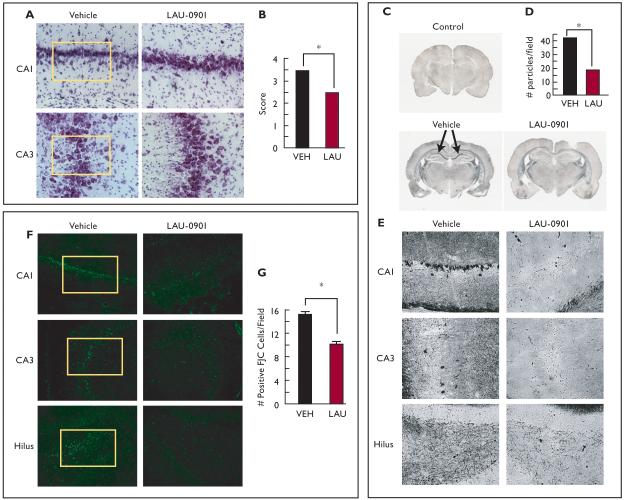
Figure 2. LAU-0901 limits hippocampal cell damage resulting from status epilepticus.
(A) Representative coronal sections of CA1 and CA3 hippocampal regions (Nissl staining, 40X) showing that LAU-0901 attenuates loss of structural organization in CA1 and CA3 observed vehicle-treated animals (box). (B) LAU-0901 reduces hippocampal damage compared with vehicle. (C) Coronal section of brain from representative control (naïve rat), vehicle, and LAU-0901-treated rats. LAU-0901 attenuates the degenerative process in hippocampi, compared with the strong staining (arrows) observed in hippocampi from vehicle-treated rats. (D, E) Representative hippocampal region of LAU-0901-treated rats showing lower dark neurons and granule density (D) in all hippocampal regions compared with vehicle-treated rats (20X). (F) Representative coronal section of CA1, CA3 and DG region of hippocampus from vehicle- and LAU-0901-treated rats using Fluoro-Jade C (FJC). Note that LAU-0901 reduces positive cells in hippocampal regions. (G) LAU-0901 limits the degeneration of neurons in the hippocampus after status epilepticus (SE) compared with vehicle (20X). Values represent averages and ± S.E.M., * = p<0.05.