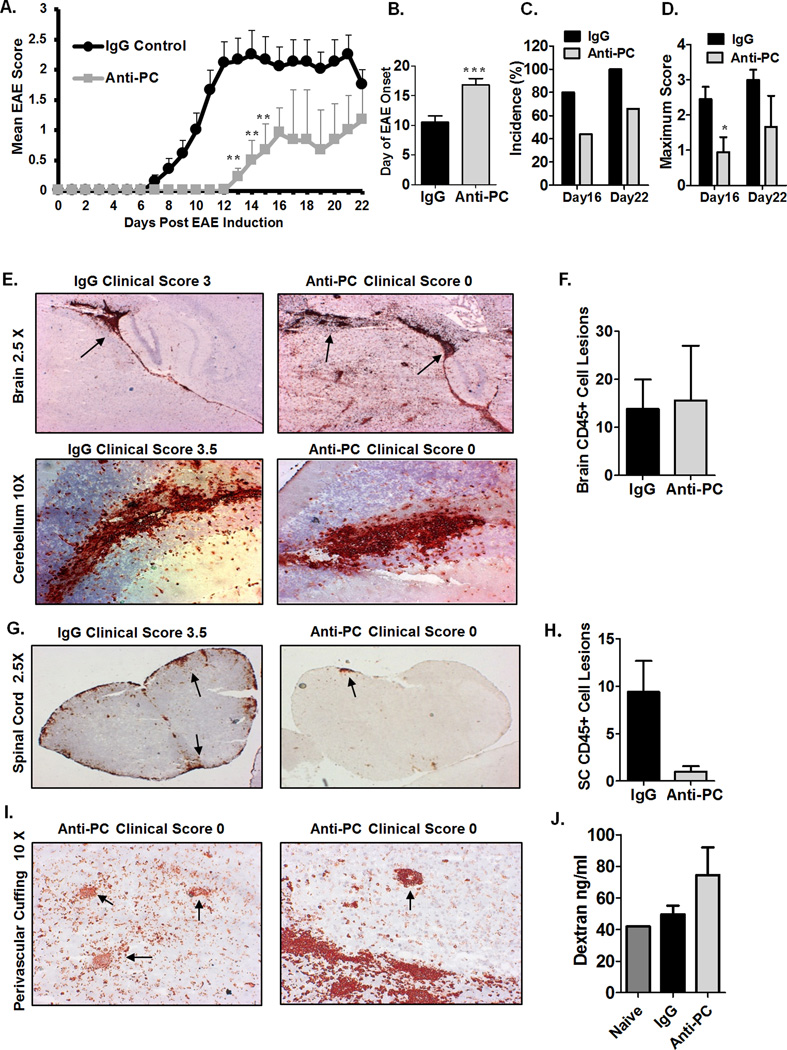
Figure 1. Mice treated with anti-PC exhibit attenuated EAE despite considerable cellular infiltration in the brain.
(A) To induce EAE, BL/6 mice were immunized with MOG35–55 in CFA; pertussis toxin was i.v. injected on the day of immunization and 48 hours later. Anti-PC or IgG was i.p. injected on days 0, 2, 4, and 6 post EAE induction. Mice were monitored daily to assess clinical signs, and scores were assigned based on the scoring system outlined in materials and methods. Scores were plotted as the mean ± S.E.M (anti-PC n = 9, IgG control n = 10. On day 16, mice from both groups were randomly selected for tissue collection. ** p < 0.01 by Mann Whitney test; Statistical analysis up to day 16 included all mice. Statistical analysis up to day 22 did not include mice taken for tissue collection on day 16). The results shown are representative of five independent experiments. (B) Day of EAE onset for each mouse from both IgG or Anti-PC group are averaged and shown with ± SEM (*** p < 0.001 by Student t test). For mice that were not showing clinical signs at the time of tissue collection, the day following tissue collection was assigned as the day of onset. (C) EAE incidence on days 16 and 22 post EAE induction is represented as percentages. The calculated incidence on Day 22 does not include the mice that were taken for tissue collection on day 16. (D) Maximum clinical score reached by each mouse from both groups were averaged and represented with ± SEM (* p < 0.05 by Student t test ). (E) Brains from both groups were harvested at the peak of disease (days 14–17) following EAE induction. Brain sections were stained with anti-CD45 (red). Arrows indicate CD45+ cell aggregates in brain sections. Images were captured using using a Zeiss Axio Imager M1 microscope. (F) CD45+ cell aggregates in brain sections of mice from both groups were individually counted at 10X magnification using a Zeiss Axio Imager M1 microscope. Counts are represented as means ± SEM (IgG n = 6, anti-PC n = 5). (G) Spinal cords from IgG or anti-PC mice were harvested at days 14–17 following EAE induction. Spinal cord sections were stained with anti-CD45 (red). Arrows indicate CD45+ cell aggregates. Images were captured using using a Zeiss Axio Imager M1 microscope. (H) CD45+ cell aggregates in spinal cord sections of mice from both groups were individually counted at 10X magnification using a Zeiss Axio Imager M1 microscope. Counts are shown as means ± SEM (IgG n = 6, anti-PC n = 5). (I) Brain sections were analyzed for CD45+ cellular infiltrates surrounding blood vessels in the brain parenchyma of anti-PC mice. Images were captured using using a Zeiss Axio Imager M1 microscope. (J) At day 5 post EAE induction, fluorescent dextran molecules (2 mg) were i.v. injected into the systemic circulation of anti-pc and IgG mice. Brains were harvested 5 hours later to assess the degree of dextran extravasation. The concentration of extravasated dextran in brain homogenates was determined based on a standard curve. Data shown as means ± SEM (IgG n = 3, anti-PC n = 2). The experiment was repeated twice with the same result.