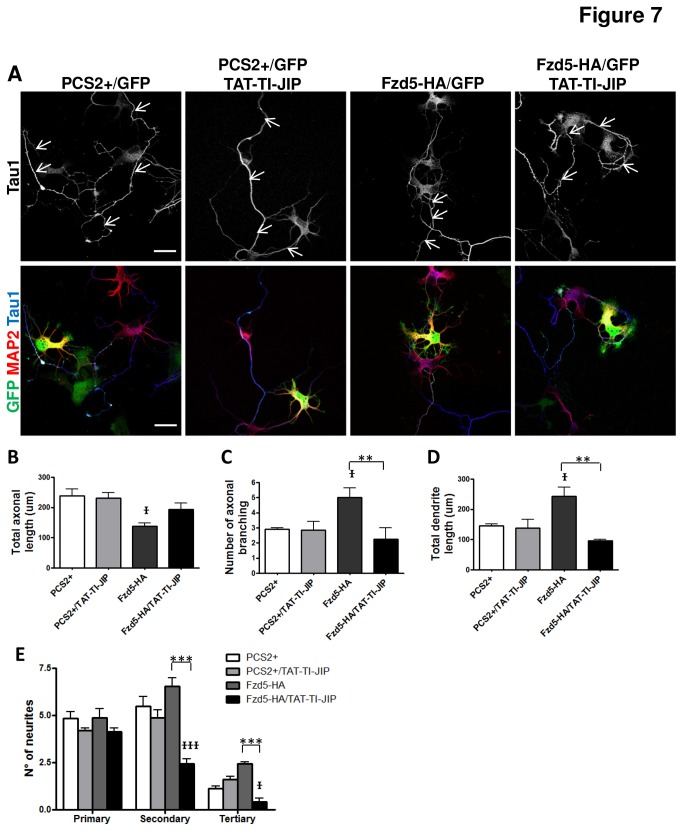
Figure 7. Effect of Fzd5 overexpression on neuronal morphology is partially prevented by a JNK inhibitor.
A. Representative images showing hippocampal neurons, transfected with the empty vector PCS2+ plus GFP as a control or Fzd5-HA plus GFP, at 2 DIV, and treated with or without the JNK inhibitor, TAT-TI-JIP. Immunodetection of the axonal marker Tau1 (upper panels) and merge (lower panels) are shown. GFP was used to detect transfected neurons and white arrows mark the quantified axons. B, C. Quantification of total axonal length (B) and axonal branching (C) of control and Fzd5-overexpressing polarized neurons, with or without treatment. Neurons overexpressing Fzd5 with polarized axonal markers showed a significant increase in axonal branching and a significant decrease in axonal length compared to control and treated control neurons. These effects were prevented by TAT-TI-JIP treatments. D, E. Quantification of total dendritic length (D) and primary, secondary and tertiary dendritic branching (E) of control and Fzd5-overexpressing polarized neurons, with or without TAT-TI-JIP treatment. Neurons overexpressing Fzd5 showed a significant increase in total dendrite length and in the number of tertiary neurites compared to that of the control and treated control neurons. TAT-TI-JIP prevented these effects and in fact decreased the number of secondary and tertiary neurites. Scale bar: 20 µm. * p< 0.05; ** p< 0.01; *** p< 0.001; τ, significantly different from the control; τ p< 0.05; ττ p< 0.01; τττ p< 0.001. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean of three independent experiments for the treated neurons and five independent experiments for the neurons without treatment.