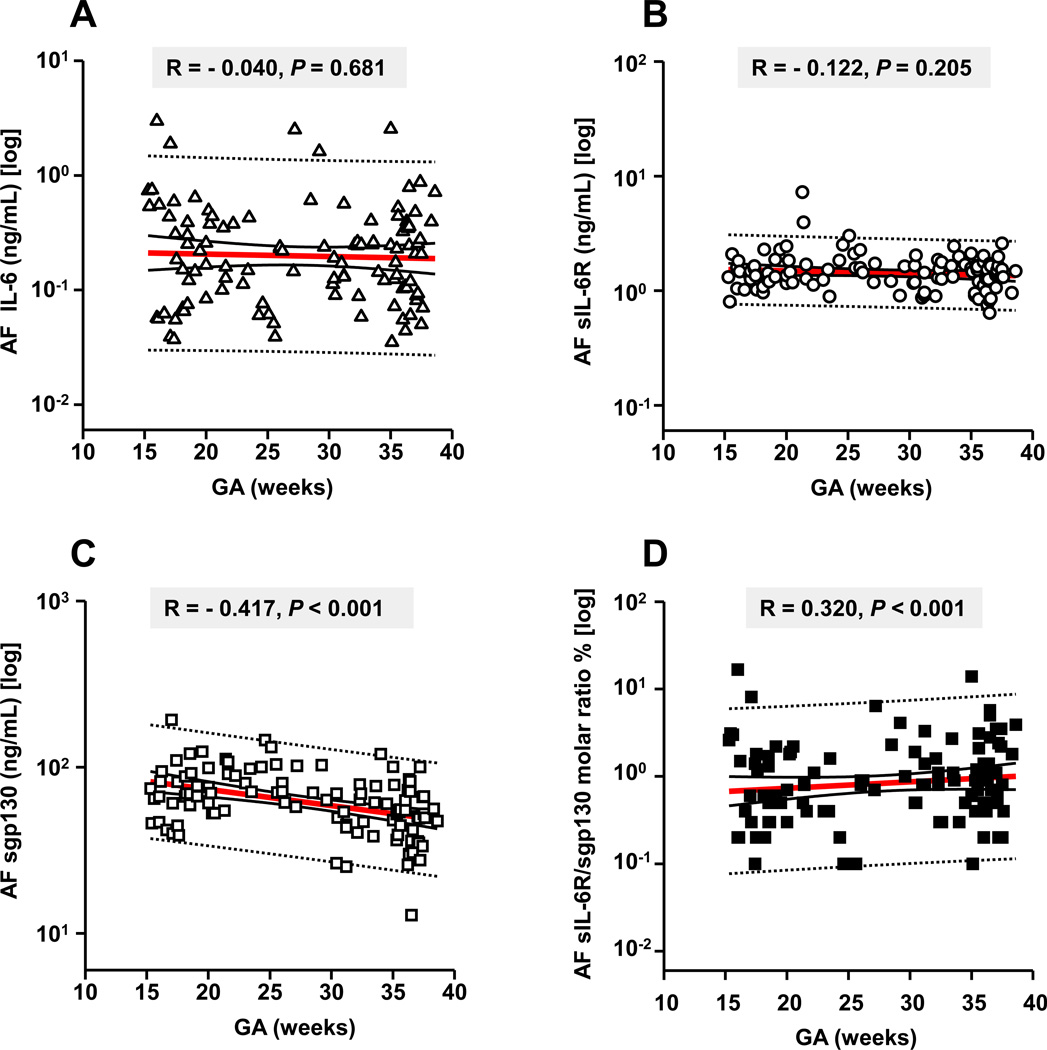
Figure 2. Relationships between amniotic fluid (AF) levels of IL-6, sIL-6R, sgp130, sIL-R/ sgp130 molar ratio and gestational age (GA) in pregnancies with normal outcomes (n=110).
We restricted this analysis to amniocenteses samples from women with normal outcomes: second trimester genetic (n=39), third trimester lung maturity (n=40) and preterm women with amniocentesis to rule-out infection who ultimately delivered at term (n=31). Data for IL-6 (x-axis of A) and sIL-6R (x-axis of B) demonstrated no significant correlations between the levels of these two analytes and GA (y-axes of all). The AF levels of sgp130 were inversely correlated with GA with significantly lower levels at term (x-axis of C). Using the two-step clustering method, we identified unbiased GA separation points that partitioned AF sgp130 concentration into 3 clusters: “high”: 104 [100–120] ng/mL, GA: 22 [18–26] weeks “mid”: 67 [60–74] ng/mL, GA: 27 [19–35] weeks and “low”: 39 [34–45] ng/mL, GA: 35 [31–37] weeks. There was a significant GA regulation of the sIL-6R/sgp130 molar ratio (x-axis of D) with higher values at term. This trend was primarily due to the decrease in sgp130 as gestation progressed. For each graph the Spearman correlation coefficient R and the level of statistical significance is shown. Data presented in logarithmic format. Panels A-D: Thick lines: 1st order regression line; Thin continuous lines: 95% confidence intervals; dotted lines: 95% prediction intervals.