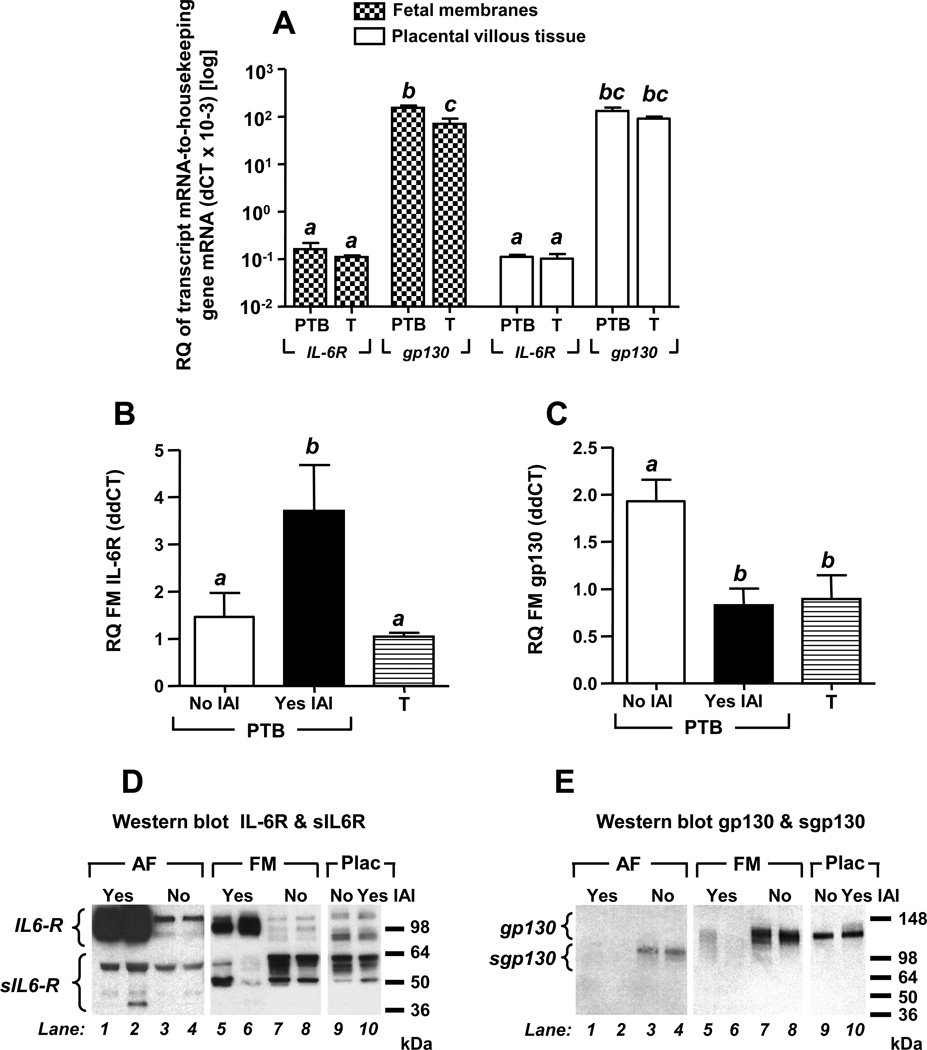
Figure 4. mRNA (quantitative RT-PCR) and protein (Western blot) expression of IL-6R and gp130.
Real time quantitative RT-PCR was used to study tissues retrieved from 9 term (T) third trimester healthy women and a subset of 20 preterm birth (PTB) cases [no intra-amniotic inflammation (IAI) & no histological chorioamnionitis n=5; yes IAI, & yes histological chorioamnionitis n=15]. IL-6R and gp130 mRNA was identified in both fetal membranes and placental villous trophoblast (A). gp130 mRNA was more abundant than the IL-6R mRNA in both fetal membranes and placental villous tissues. In the fetal membranes the gp130 mRNA levels were significantly decreased at term (T). There was a significant increase in IL-6R mRNA (B) and a significant decrease in the expression of gp130 (C) in the fetal membranes of women with IAI. Relative quantitation (RQ) ΔCT values are reported relative to expression of the housekeeping genes for each tissue (A). ΔΔCT RQ values were reported relative to a reference RNA pool of the same tissue (B-C). Data presented as mean + SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Student-Newman-Keuls tests. Means marked with different superscripts are statistically significant (P<0.05). Panels D and E show representative Western blots of AF (AF), fetal membrane (FM) and placental (Plac) proteins. Membranes were probed with compatible polyclonal anti-IL-6R (D) or monoclonal anti-gp130 antibody (E). Specificity was confirmed in identical blots with omitted primary antibodies.