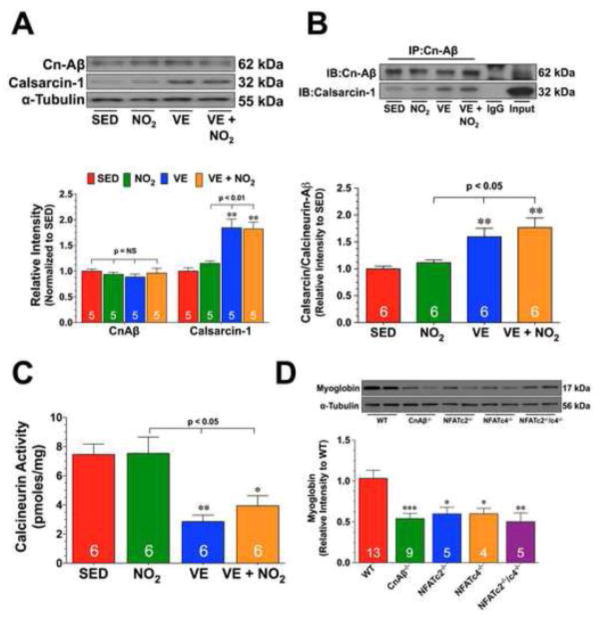
Fig. 5. Exercise Training Increases the Expression of Calsarcin-1.
(A) Representative immunoblots and densitometric analysis of calcineurin Aβ (CnAβ) and calsarcin-1 from the hearts of SED, NO2, VE, and VE+NO2 mice. (B) Representative immunoblots and densitometric analysis of the interaction of CnAβ with calsarcin-1 from the hearts of SED, NO2, VE, and VE+NO2 mice. For these experiments, heart homogenates were immunoprecipitated with a CnAβ antibody. The samples were then subjected to standard Western blot techniques and the membranes probed with CnAβ and calsarcin-1 antibodies to reveal the interaction. (C) Calcinuerin activity (pmoles/mg) from the hearts of SED, NO2, VE, and VE+NO2 mice. (D) Representative immunoblots and densitometric analysis of myoglobin from the hearts of Wild-type (WT), CnAβ deficient (CnAβ−/), NFATc4 deficient (NFATc4−/−), NFATc2 deficient (NFATc2−/−), and NFATc2/NFATc4 double deficient (NFATc2−/−/c4−/−) mice. Numbers inside the bars are the number of animals investigated. Values are means ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 vs. SED or WT.