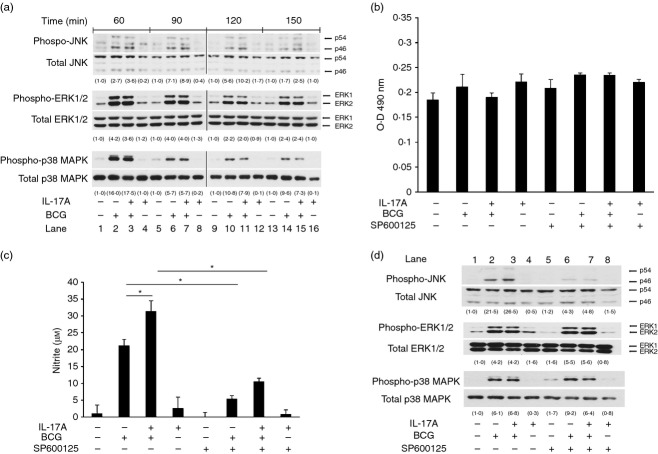
Figure 2.
Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) specifically enhances activation of Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, but not extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, during BCG infection. (a) Macrophages were pre-treated with IL-17A (25 ng/ml) for 24 hr, followed by BCG infection at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 1. At indicated time-points, whole cell lysates were collected for Western blot analysis of JNK, ERK1/2 or p38 MAPK. The data were representative of three independent experiments. (b) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay for cell viability in the presence of SP600125. Macrophages were incubated with JNK inhibitor SP600125 (10 μm) for 1 hr, followed by IL-17A (25 ng/ml) pre-treatment for 24 hr. The macrophages were then infected by bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) at an MOI = 1 for another 24 hr. The culture supernatants were collected for determination of LDH release. The data represented mean ± SE of three independent experiments. (c) Inhibition of JNK pathway suppresses IL-17-enhanced nitric oxide (NO) production in BCG-infected macrophages. Macrophages were treated as described in (b).The culture supernatants were collected for determination of NO by Griess reaction. The data represented mean ± SE of three independent experiments. *P < 0·05. (d) Analysis of specificity of SP600125. Macrophages were incubated with JNK inhibitor SP600125 (10 μm) for 1 hr, followed by IL-17A (25 ng/ml) pre-treatment for 24 hr. The macrophages were then infected by BCG at an MOI = 1 for another 60 min. Whole cell lysates were collected for Western blot analysis of JNK, ERK1/2 or p38 MAPK. The data were representative of three independent experiments. The determination of the intensities of protein bands was assisted by imageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). The intensities of phosphorylated proteins were normalized to the corresponding total proteins. The values in parentheses were relative intensities compared with untreated control.