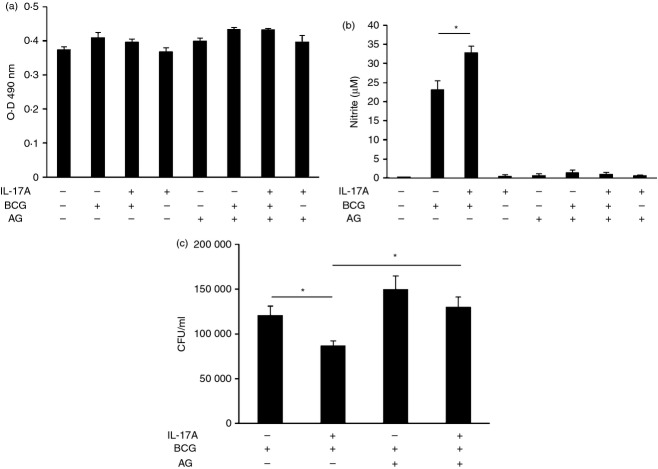
Figure 6.
Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) -enhanced clearance of intracellular bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) is dependent on nitric oxide (NO). (a) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay for cell viability in the presence of aminoguanidine (AG). Macrophages were incubated with Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor AG (100 μg/ml) for 1 hr, followed by IL-17A (25 ng/ml) pre-treatment for 24 hr. The macrophages were then infected by BCG at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 1 for another 48 hr. The culture supernatants were collected for determination of LDH release. The data represented mean ± SE of three independent experiments. (b) NO production in BCG-infected macrophages in the presence of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) inhibitor. Macrophages were incubated with AG (100 μg/ml) for 1 hr, followed by IL-17A (25 ng/ml) pre-treatment for 24 hr. The macrophages were then infected by BCG at MOI = 1. The culture supernatants were collected after 24 hr of BCG infection for determination of NO by Griess reaction. The data represented mean ± SE of four independent experiments. *P < 0·05. (c) Intracellular survival of BCG in macrophages in the presence of iNOS inhibitor. The macrophages were treated as described in (b). After 48 hr of BCG infection, non-phagocytosed bacteria were washed. Intracellular BCG was recovered by lysis of the macrophages and plated onto 7H10 agar. Colony-forming units (CFU) were enumerated after 3 weeks of incubation. The data represented mean ± SE of four independent experiments. *P < 0·05.