Abstract
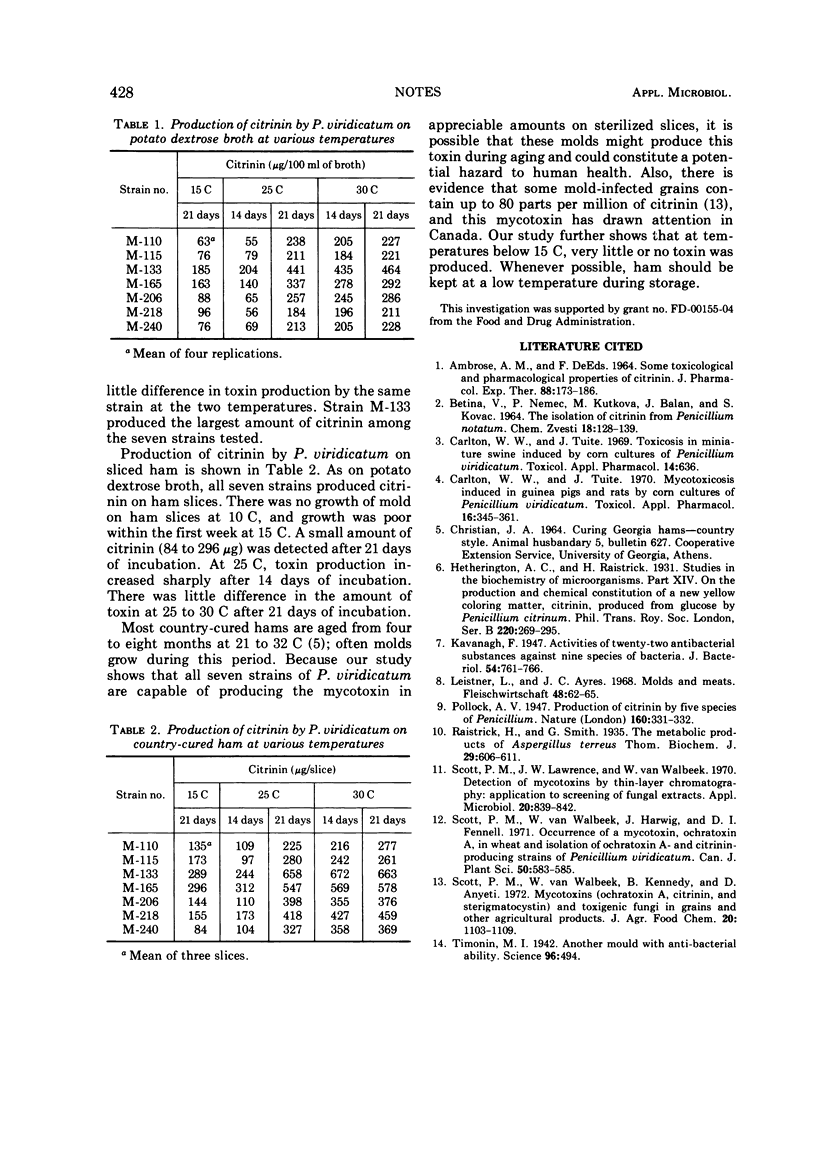
Seven strains of Penicillium viridicatum isolated from country-cured ham produced citrinin in potato dextrose broth and on country-cured ham. None of the strains produced detectable amounts of citrinin at 10 C. The optimal temperature range for citrinin production was 25 to 30 C.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlton W. W., Tuite J. Mycotoxicosis induced in guinea pigs and rats by corn cultures of Penicillium viridicatum. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970 Mar;16(2):345–361. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(70)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanagh F. Activities of Twenty-two Antibacterial Substances against Nine Species of Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1947 Dec;54(6):761–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raistrick H., Smith G. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms: The metabolic products of Aspergillus terreus Thom. A new mould metabolic product-terrein. Biochem J. 1935 Mar;29(3):606–611. doi: 10.1042/bj0290606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. M., Lawrence J. W., van Walbeek W. Detection of mycotoxins by thin-layer chromatography: application to screening of fungal extracts. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Nov;20(5):839–842. doi: 10.1128/am.20.5.839-842.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. M., Van Walbeek W., Kennedy B., Anyeti D. Mycotoxins (ochratoxin A, citrinin, and sterigmatocystin) and toxigenic fungi in grains and other agricultural products. J Agric Food Chem. 1972 Nov-Dec;20(6):1103–1109. doi: 10.1021/jf60184a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonin M. I. ANOTHER MOULD WITH ANTI-BACTERIAL ABILITY. Science. 1942 Nov 27;96(2500):494–494. doi: 10.1126/science.96.2500.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


