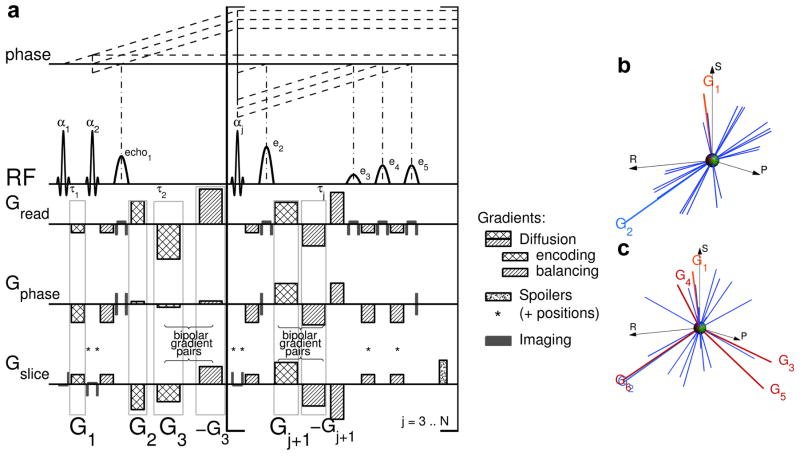
Figure 1.
MEDITATE diffusion tensor acquisition technique. a) The N sinc-shaped slice selective RF-pulses with flip angles αj separated by time constants τj generate a series of (N − 2) × 4 + 1 separate echoes, according to the plotted coherence pathways (dashed lines, only reflecting RF induced phase changes and only including eventually refocused echoes). Each of these echoes carries a different diffusion weighting and direction, as encoded by the diffusion gradient vectors G⃗j, j = 1..(N + 1) (checkered areas) and their associated rebalancing gradients (hatched areas). Spoiler gradients (speckled areas and included in other gradients on positions labeled *) spoil the remainders of the not retained coherence pathways. (The gradient areas reflect the actual gradient moments whose durations along different physical axes are slightly unequal to minimize slew rate gradient stimulation effects.) b,c) Visual representation of the gradient vectors and the normalized diffusion directions (blue lines, [25,26]) encoded by only G⃗1 and G⃗2 (b) and by all diffusion gradients G⃗j, j = 1..(N +1) (c). In (b), the diffusion directions populate a single plane determined by G⃗1 and G⃗2, gradients G⃗j, j = 3..(N + 1) push the diffusion directions out of this plane (c) in order to sample all diffusion directions.