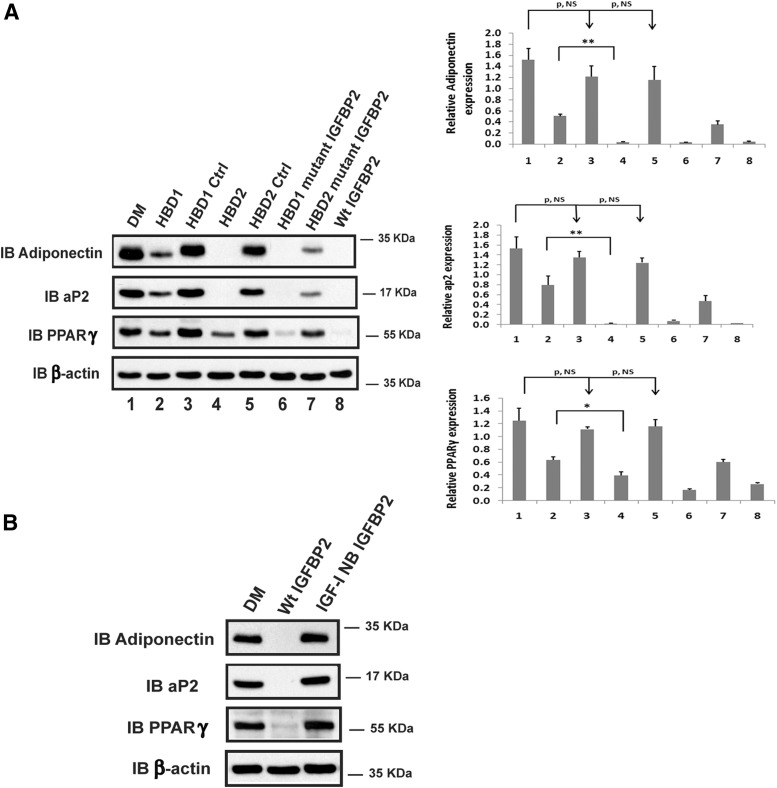
Figure 1.
IGFBP-2 and its HBDs inhibit the differentiation of preadipocytes isolated from IGFBP-2 null mice. (A) Primary preadipocytes from IGFBP-2−/− mice were isolated from inguinal fat pads following the procedure described in Materials and Methods. Two days after reaching confluence, cells were treated with differentiation medium (DM) (lanes 1–8). This medium was then supplemented with HBD1 peptide (HBD1, lane 2), scrambled HBD1 peptide (HBD1 Ctrl [Control], lane 3), HBD2 peptide (HBD2, lane 4), IGFBP-5 C-terminal HBD peptide (HBD2 Ctrl, lane 5), IGFBP-2 protein with mutated HBD1 sequence (HBD1 mutant IGFBP-2, lane 6), IGFBP-2 with mutated HBD2 sequence (HBD2 mutant IGFBP-2, lane 7), or native IGFBP-2 (WT IGFBP-2, lane 8). The cell lysates were immunoblotted (IB) with antiadiponectin, aP2, and PPARγ antibodies, respectively. As a loading control, the blots were IB with an anti-β-actin antibody. Quantitative analysis of the results from 3 separate experiments was performed, and the results are expressed in relation to β-actin expression. Each value represents mean ± SE. *, P < .05 and **, P < .01 denotes a significant difference between 2 treatments. P, NS indicates no significant difference between 2 treatments. (B) Preadipocytes isolated from IGFBP-2−/− mice were treated with either DM, DM plus WT IGFBP-2 (Wt IGFBP-2), or DM plus IGF-I nonbinding IGFBP-2 (IGF-I NB IGFBP-2). The cell lysates were IB with antiadiponectin, aP2, and PPARγ antibodies, respectively. As a loading control, the blots were IB with an anti-β-actin antibody.