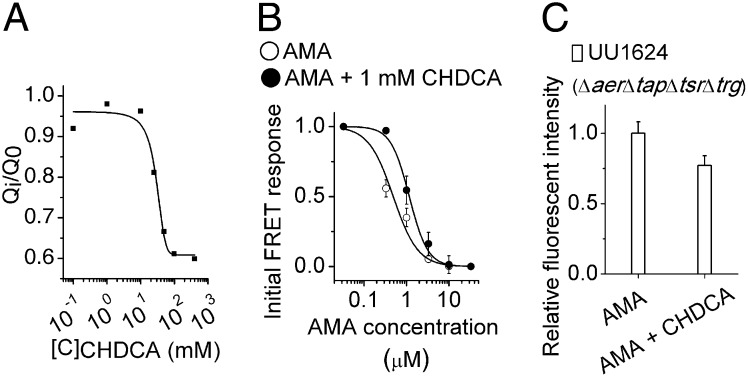
Fig. 4.
Detection of the antagonist function of CHDCA. (A) Competitive ITC binding assay. CHDCA competes with AMA for Tar periplasmic domain binding. The WT Tar periplasmic domain was incubated with different concentrations of CHDCA, and the total heat released from its binding to AMA (Qi) were measured. Q0 was the total heat released from AMA binding to the same concentration of the Tar periplasmic domain without CHDCA. (B) Responses of the Tar-only strain to different AMA concentrations with or without 1 mM CHDCA (mean ± SEM; n ≥ 2) measured by FRET. Data are fitted by the Hill model. (C) The responses of UU1624 cells to the same gradient of AMA with or without 1 mM CHDCA (mean ± SEM; n = 12; P = 0.044, Student two-tailed unpaired t test). The presence of CHDCA reduces the chemotactic response to the AMA gradient.