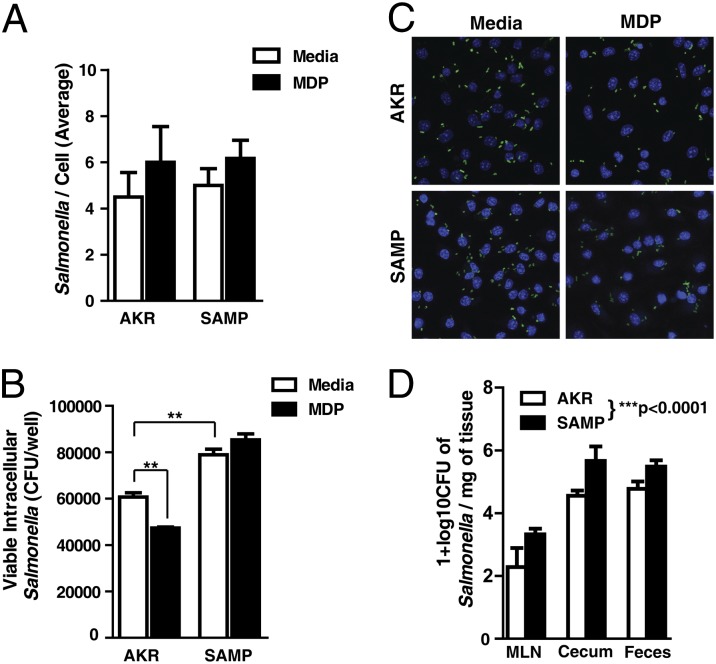
Fig. 5.
SAMP BMDMs have impaired intracellular bacterial killing and are unresponsive to MDP stimulation. BMDMs from preinflamed SAMP and AKR mice were infected with Salmonella typhimurium for 90 min in the presence and absence of MDP (10 μg/mL). (A) Quantification of immunofluorescent micrographs stained for total number of Salmonella per cell (six fields counted from two separate experiments; mean ± SEM). (B) Viable intracellular Salmonella recovered in gentamicin protection assays. (C) Confocal micrographs of infected BMDMs. Salmonella shown in red, and nuclei stained with DAPI (blue) (six independent experiments; mean ± SEM). The double asterisk (**) denotes significant differences at P < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA, pairwise Bonferroni). (D) SAMP and AKR mice were pretreated with streptomycin and infected with 109 CFU of Salmonella or with sterile PBS; bacterial loads from mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs), cecum, and feces were calculated 2 d postinfection. SAMP mice were significantly more likely to yield higher Salmonella counts than AKR [linear regression, F(4,23), P < 0.00001, adjusted R2 = 0.7891].