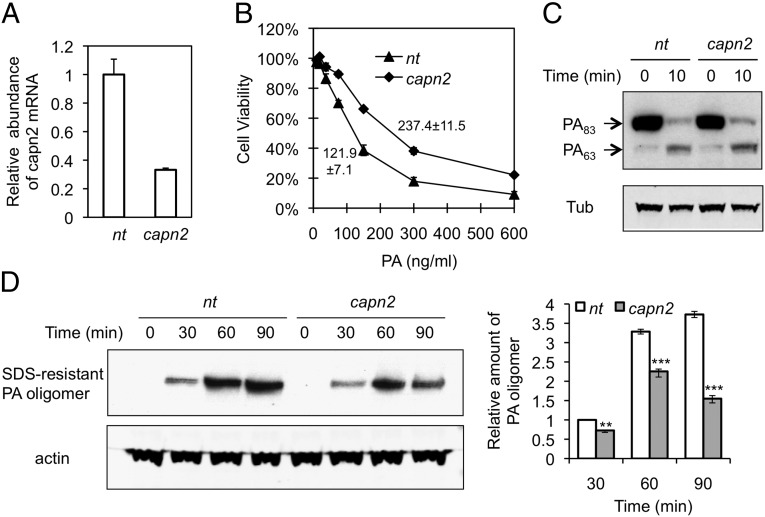
Fig. 4.
Effect of capn2 deficiency on PA internalization. RAW264.7 cells were infected with lentivirus expressing capn2 shRNA or nontargeting shRNA (nt). (A) The capn2 mRNA expression determined by quantitative RT-PCR was normalized to the expression of β-actin. Data represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (B) Cellular susceptibility to PA-LF. The cells were exposed for 4 h to a mixture containing the indicated concentration of PA and 200 ng/mL LF; then cell survival was determined by MTT assay. The percent of cell viability is represented as mean ± SD. Data are from one representative experiment (n = 3) carried out in triplicate. LD50 values of PA in cells infected with lentivirus expressing nt or capn2 shRNA are 121.9 ± 7.1 ng/mL and 237.4 ± 11.5 ng/mL, respectively. P < 0.01. (C) Binding and processing of PA. The cells were exposed to 1 µg/mL PA at 4 °C for 1 h and then were shifted to 37 °C for 10 min. Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-PA antibody. Tub, tubulin. (D) PA-internalization assay. Cells were exposed to 1 µg/mL PA at 37 °C for the indicated time, and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-PA antibody as a probe. (Left) A representative blot. (Right) Relative abundance of SDS-resistant PA oligomers was quantified by normalization to actin in three independent experiments; data are shown as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 compared with nt.