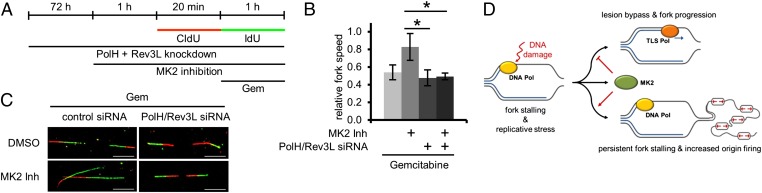
Fig. 4.
Rescue of gemcitabine-induced slow replication fork speed by MK2 inhibition depends on TLS. (A) Labeling protocol for DNA fiber analysis. Cells were depleted of PolH and Rev3L. At 72 h later, cells were pretreated with MK2 inhibitor or DMSO for 1 h and then pulse-labeled with CldU for 20 min. Afterward, cells were pulse-labeled with IdU for 1 h and simultaneously exposed to 400 nM gemcitabine. (B) Average relative replication fork speed (ratio of length of IdU-labeled vs. length of CldU-labeled tracks) in gemcitabine-treated cells in dependence of MK2 inhibition and depletion of TLS polymerases PolH and Rev3L (n = 3; *P = 0.0308 and *P = 0.0186, respectively). (C) Representative images of fibers from cells treated with gemcitabine as in A (Scale bar: 10 µm.) (D) A model of how, upon replicative stress, the decision between TLS and replication fork stalling and increased origin firing is regulated by MK2.