Fig. 3.
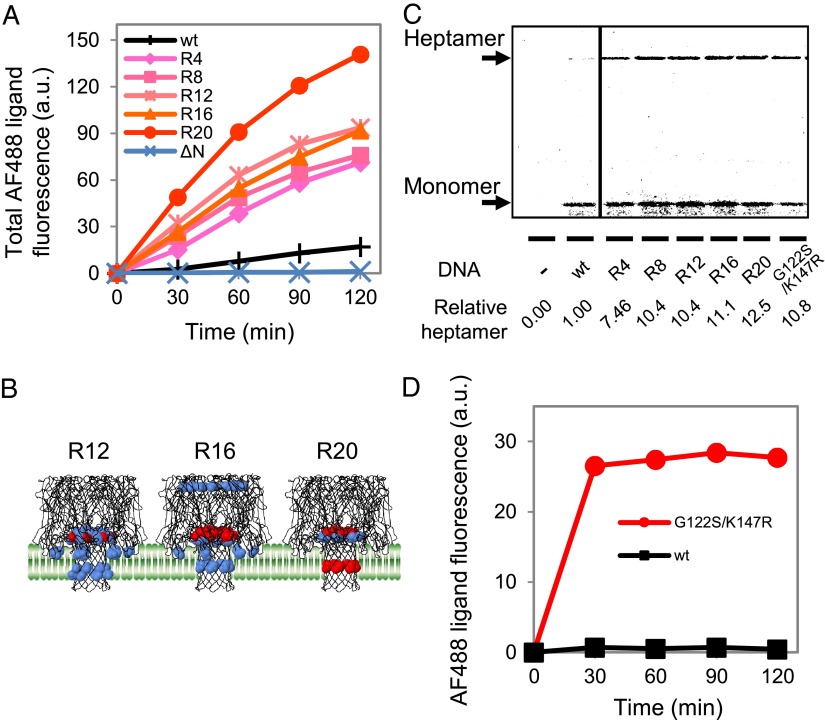
Properties of the AH mutants obtained after multiple rounds of liposome display. (A) Time course of AF488 ligand accumulation for the various AH gene pools. R4 represents the gene pool obtained after R4 of screening (similarly for R8 and others). The vertical axis is the sum of the AF488 ligand fluorescence intensity of GUVs measured by FACS (Fig. S3A). The values at time 0 were set to zero. (B) Locations of the fixed mutations among the selected clones mapped on the 3D structure of the WT AH. A model membrane is also depicted. The mutations found in more than 10% and 25% of the clones are shown in blue and red, respectively. (C) Binding of the AH variants to the GUVs. The AH variants were synthesized on the exterior of the GUVs with the PURE system supplemented with [35S]methionine and 15 pM DNA. After removing the unbound proteins, the GUV fraction was subjected to SDS/PAGE without boiling, allowing for the quantitative analysis of both heptamers and monomers (18, 22, 23). (D) Pore-forming activities of the WT AH and G122S/K147R mutant with purified proteins. Purified AH (150 nM) was added to the HaloTag protein-encapsulated GUVs, and the AF488 ligand was added to the exterior of the GUVs. The measurement and analysis were performed as described for A.