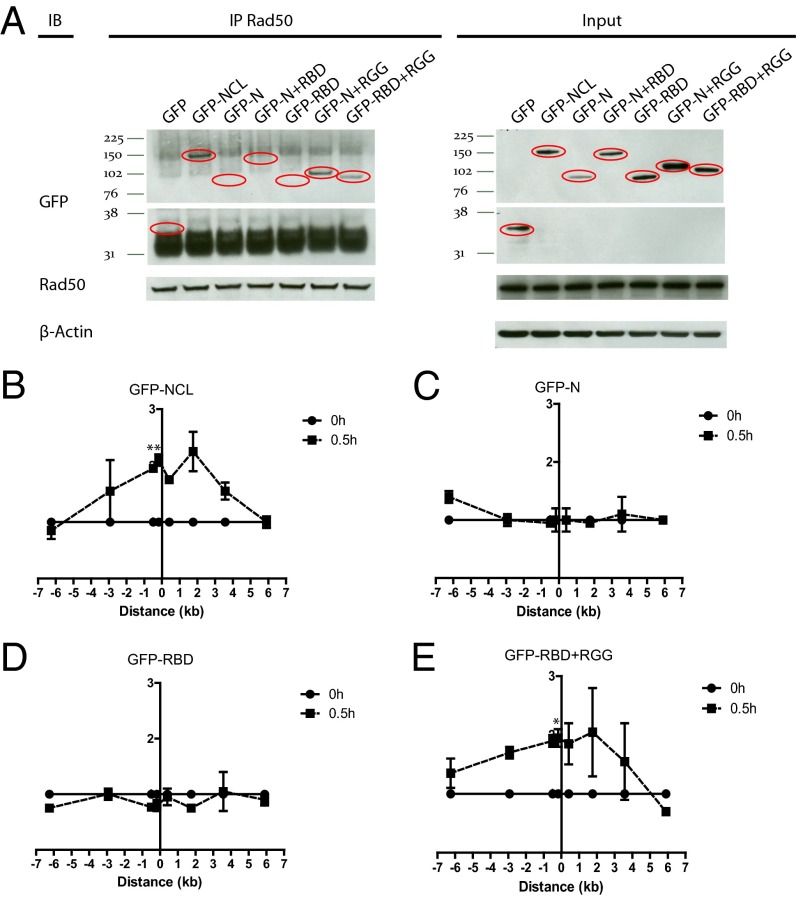
Fig. 6.
The C-terminal RGG domain of nucleolin is responsible for the interaction with RAD50 and the recruitment of nucleolin to the DSB. (A) Nucleolin interacts with RAD50 via its RGG domain. Coimmunoprecipitation of RAD50 and indicated nucleolin-deletion mutants in MCF7 cells transiently transfected with GFP or GFP-tagged wild-type nucleolin or nucleolin-deletion mutants. (B–E) The RGG domain is required for nucleolin recruitment to the DSB. ChIP showing recruitment of wild-type nucleolin or indicated nucleolin-deletion mutants in MCF7 cells stably expressing ddI-PpoI as described in Fig. 1B that were transiently transfected with wild-type nucleolin or nucleolin-deletion mutants. Anti-GFP antibody was used to precipitate GFP-tagged wild-type nucleolin and nucleolin-deletion mutants. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.