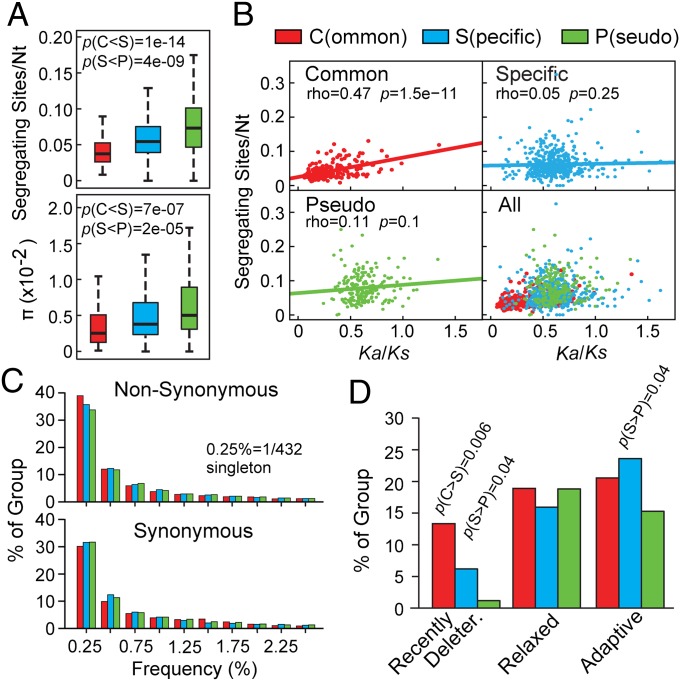
Fig. 1.
SNP analyses of Common, Specific, and Pseudo FBX genes from 432 Arabidopsis accessions. (A) Comparisons of sequence polymorphism (segregating sites per nt) (Upper) and diversity (average nt differences per site, π) (Lower). Each box plot shows the median (solid line), the 25th and 75th percentiles (boxes), and the fifth and 95th percentiles (dashed lines). (B) Spearman rank correlation test between sequence polymorphism and natural selection (Ka/Ks). Correlation coefficients (rho), P values, and lines of best-fit linear regression are included. (C) Frequency spectrum of rare alleles with nonsynonymous and synonymous mutations. (D) Distribution of recently deleterious (MAF < 5%), relaxed, and adaptive mutations (McDonald–Krietman test). P values in A and D were calculated by Wilcoxon rank and Fisher’s exact tests, respectively.