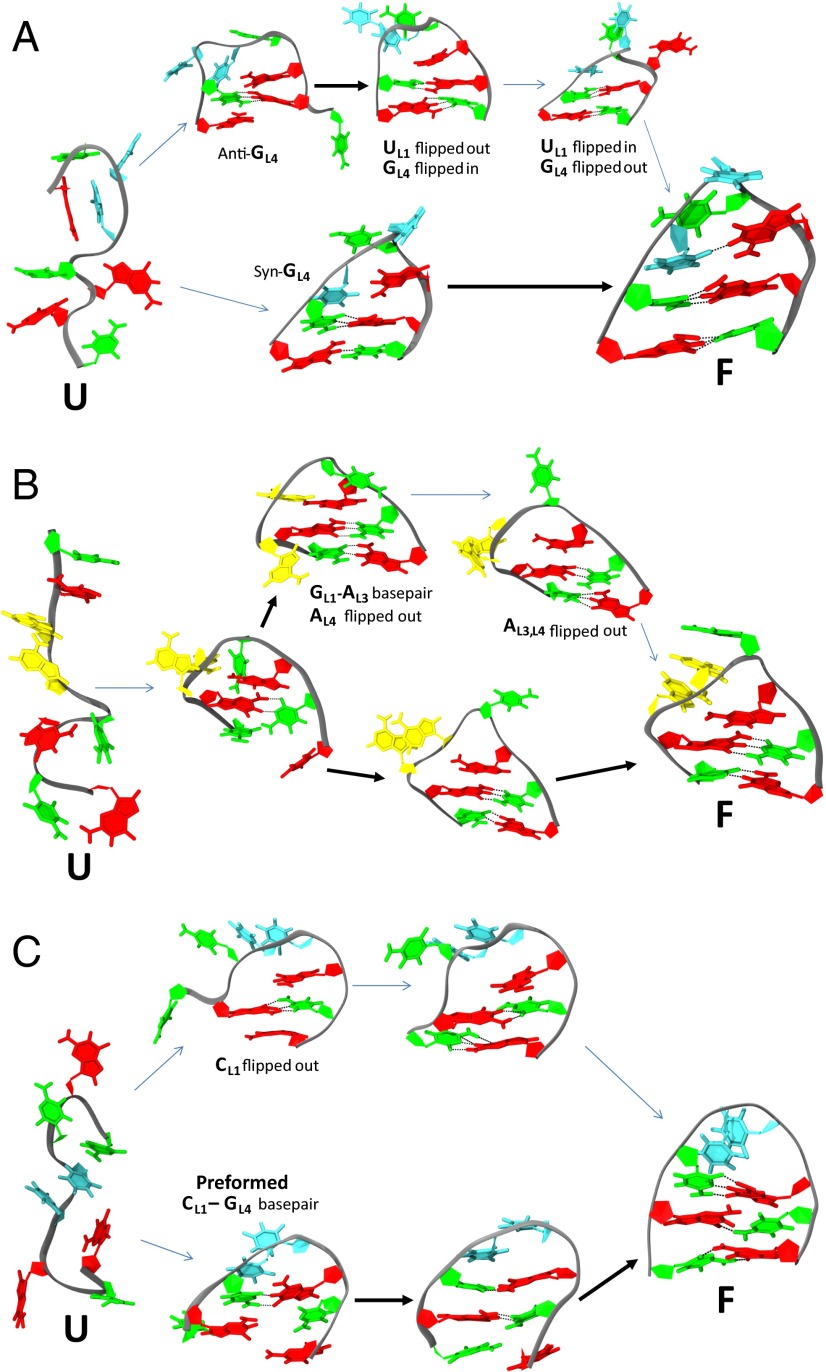
Fig. 3.
Tetraloop folding pathways. Two alternate folding pathways are observed for all three hyperstable tetraloops. Thick and thin arrows depict rapid and slow transitions, respectively. Bases are colored the same as in Fig. 2. (A) UUCG folds rapidly if GL4 is already in syn before collapse, which is required to form the trans-GU wobble base pair (lower pathway). In contrast, misfolds containing the anti-GL4 must flip GL4 out of the loop to access the syn conformation and then flip back in to pair with UL4 (upper pathway). (B) GCAA folds rapidly when GL1 correctly pairs with AL4 after loop collapse to form a sheared base pair (lower pathway), but it can also form a nonnative GL1-AL3 base pair (upper pathway). AL3 must flip out before the native GL1-AL4 base pair can form. (C) The CUUG tetraloop rapidly folds when the CL1-GL4 base pair is preformed before collapse (lower pathway); otherwise, CL1 is initially flipped out and must flip back into the loop to reach the native state (upper pathway).