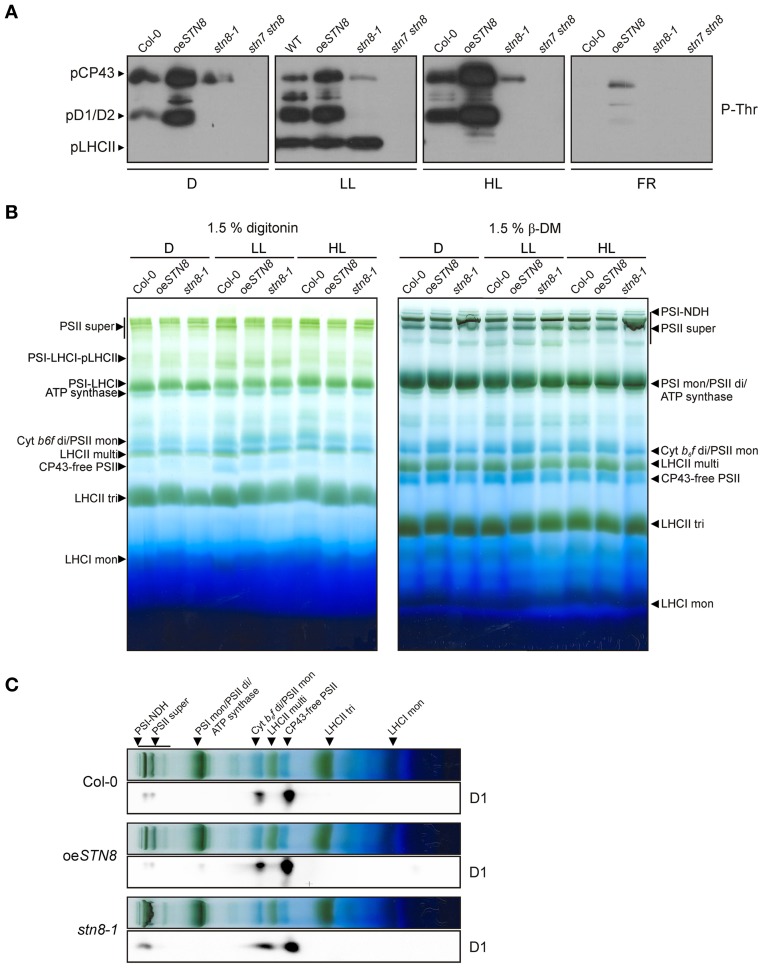
Figure 6.
Effects of altered STN8 levels on thylakoid phosphorylation and PSII supercomplex formation. (A) Thylakoid protein phosphorylation in WT (Col-0), oeSTN8, stn8-1, and stn7 stn8 plants dark-adapted for 18 h (D), subsequently transferred to LL (80 μmol photons m−2s−1) for 2 h and for additional 2 h to FR or 4 h to HL (1,000 μmol photons m−2s−1). After these light treatments, isolated thylakoids were analyzed by immunodetected using phosphothreonine (pThr) -specific antibodies (Cell Signaling). The positions of phosphorylated LHCII (pLHCII), CP43 (pCP43) and D1/2 (pD1/2) are indicated by black arrowheads. (B) Patterns of protein complexes solubilized from WT (Col-0), oeSTN8 and stn8-1 thylakoids and separated on BN-PA gels. Thylakoid membranes of WT, oeSTN8 and stn8-1 plants exposed to either LL (80 μmol photons m−2s−1) or HL (1,200 μmol photons m−2s−1) for 2 h, or kept in the dark for 18 h, were solubilized with 1.5% digitonin (left panel) or 1.5% β-DM (right panel) and separated by BN-PAGE. Protein-Chl complexes are indicated by black arrowheads. The bands detected were identified as specific protein complexes in accordance with previously published profiles (Armbruster et al., 2013): PSI-LHCI-pLHCII supercomplex (PSI-LHCI-pLHCII), PSI-LHCI supercomplex (PSI-LHCI), PSI-NDH supercomplex (PSI-NDH), PSII supercomplexes (PSII super), PSI monomers and PSII dimers (PSI mon and PSII di), PSII monomers and dimeric Cyt b6f (PSII mon and Cyt b6f di), PSII monomers w/o CP43 (CP43-free PSII), multimeric (LHCII multi), trimeric (LHCII tri) and monomeric (LHCII mon) LHCII. (C) BN-PAGE lanes bearing HL-treated samples corresponding to those shown in the right panel of (B) were subjected to SDS-PAGE in the second dimension and probed with D1-specific antibodies.