Figure 3. Inhibition of Kinesin-5 by small-molecule inhibitor or knockdown in eukaryotic cells.
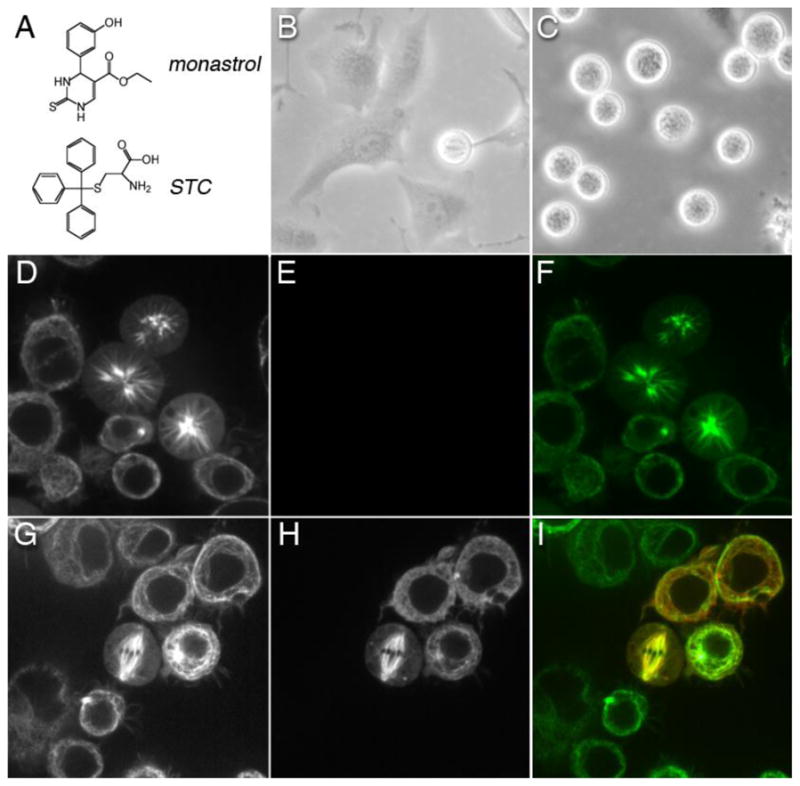
(A) Chemical structure of monastrol and S-trityl-L-cysteine (STC), which are two allosteric inhibitors of human Kinesin-5. After seeding at a density of 1x106 cells and a 24 hr incubation, human HeLa cells were treated with either (B) DMSO or (C) 1 mM STC. Rounded cell shape is diagnostic of live cells in metaphase. From cell counts, 4% of DMSO-treated cells were in metaphase, whereas 43% of STC-treated cells were in metaphase after a 12 hour-long incubation with this drug. Images (B–C) were acquired using a Nikon ELWD 0.3 phase contrast microscope under 10X magnification. Kinesin-5 (Klp61F) dsRNAi knockdown in Drosophila S2 cells expressing tubulin-GFP prevented morphogenesis of bipolar spindles and, instead, exhibited mono-polar arrays. (D) Confocal fluorescence images of living S2 cells expressing tubulin-GFP after dsRNAi knockdown of native Klp61F. The green (GFP) channel of cells displaying aberrant mono-polar mitosis is shown. (E) Red channel of cells in Panel D showing no detectable expression of Klp61F-mKATE chimera. (F) Merge of panels D and E. (G) Tubulin-GFP expression in Klp61F dsRNAi cells transfected with Klp61F-mKATE chimera. Shown is a confocal image of a rescued bipolar spindle in a living transfected cell. (H) Red channel of cells in panel G showing Klp61F-mKATE localization in transfected cells, with untransfected cells nearby. (I) Merge of panels G and H. Images (D–I) were acquired using a Zeiss Axiovert 200 inverted microscope equipped with a Yokogawa spinning disk confocal accessory. 10 X 63x/1.4 oil DIC.
